NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes
NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes
NCERT Exemplar for class 12 biology biotechnology principles and processes will aid in deepening the knowledge of students related to the topic of Biotechnology Principles and Processes. This provided exemplar by SimplyAcad allows learners to cover up all the sections presented in the chapter 11 of the biology textbook. There are MCQs based, very short, and long answer type answer questions to ensure students understand the concepts better for class 12 biology biotechnology principles and processes. It will be beneficial for students, they can prepare their own study and revision notes from them. Students can easily access this NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology in this article below to perform incredibly well in their upcoming 12th board examinations. Apart from these there are several NCERT exemplar for class 12 science of all the chapters provided in a detailed manner.
Access the NCERT Exemplar class 12 biology biotechnology principles and processes
MCQ Questions
1. Rising of dough is due to:
a. Multiplication of yeast
b. Production of CO2
c. Emulsification
d. Hydrolysis of wheat flour starch into sugars.
Ans: Rising of dough is due to the presence of CO2. Yeast present in the dough consumes the sugar present in the dough and releases carbon dioxide and ethanol. Gluten traps the released CO2 inside the dough. Thus, the dough has risen.
Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
2. Which of the following enzymes catalyze the removal of nucleotides from the ends of DNA?
a. endonuclease
b. exonuclease
c. DNA ligase
d. Hind – II
Ans: Exonuclease is the enzyme which removes nucleotides from the ends of the DNA.
Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
3. The transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another through the mediation of a viral vector is termed as:
a. Transduction
b. Conjugation
c. Transformation
d. Translation
Ans: The transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another through the mediation of a viral vector is termed Transduction.
Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
4. Which of the given statements is correct in the context of visualizing DNA molecules separated by agarose gel electrophoresis?
a. DNA can be seen in visible light
b. DNA can be seen without staining in visible light
c. Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen in visible light
d. Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen under exposure to UV light
Ans: During gel electrophoresis, we stain the DNA with Ethidium bromide. After running the gel, we observe the stained DNA under UV light because it cannot be seen in visible light, whether stained or not.
Hence, option (d) is the correct choice.
5. ‘Restriction’ in Restriction enzyme refers to:
a. Cleaving of the phosphodiester bond in DNA by the enzyme
b. Cutting of DNA at specific position only
c. Prevention of the multiplication of bacteriophage by the host bacteria
d. All of the above
Ans: The enzyme which is obtained from bacteria that can recognize specific base sequences in DNA and restrict (cut) the DNA at the specific site. Bacteria use restriction enzymes to protect themselves from a viral infections such as bacteriophages. When viruses infect the bacteria, the phage inserts its DNA into the bacterial cell for replication at that time the restriction enzyme prevents the replication of the phage DNA by cutting it into pieces. Because of this ability, they are named restriction enzymes. It hydrolyses a phosphodiester bond on one of the two DNA strands.
Hence, option (d) is the correct choice.
6. Which of the following is not required in the preparation of a recombinant DNA molecule?
a. Restriction endonuclease
b. DNA ligase
c. DNA fragments
d. E.coli
Ans: Restriction endonuclease recognize a specific site of a DNA sequence and cleaves the DNA at the target sequence.
DNA ligase attaches two DNA strands.
E. coli is a bacteria which is used in various experiments.
Hence, option (d) is the correct choice.
7. In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA molecules are separated based on recognizes their:
a. Charge only
b. Size only
c. Charge to size ratio
d. All of the above
Ans: Gel electrophoresis is the method by which mixtures of DNA, RNA, or proteins are separated according to their molecular size.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
8. The most important feature in a plasmid to serve as a vector in a gene cloning experiment is:
a. Origin of replication (ori)
b. Presence of a selectable marker
c. Presence of sites for restriction endonuclease
d. Its size
Ans: The most important feature in a plasmid to serve as a vector in thatene cloning experiments is the origin of replication (ori). It is a sequence from where replication starts. When a piece of DNA is linked to this ori it replicates the DNA and makes multiple copies within the host cell as well as it also controls the copy number of the linked DNA.
Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
9. While isolating DNA from bacteria, which of the following enzymes is not required?
a. Lysozyme
b. Ribonuclease
c. Deoxyribonuclease
d. Protease
Ans: Deoxyribonuclease is the enzyme that is not used while isolating DNA from bacteria.
Lysozyme is used for breaking the membranes which surround DNAs.
Ribonuclease is used for removing RNA.
Protease is used for removing protein.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
10. Which of the following contributed in popularising the PCR (polymerase chain reactions) technique?
a. Easy availability of DNA template
b. Availability of synthetic primers
c. Availability of cheap deoxyribonucleotides
d. Availability of ‘Thermostable’ DNA polymerase
Ans: Thermostable DNA is obtained from Thermus aquaticus bacteria. It remains active at high temperatures thus helping in the denaturation of DNA during PCR.
Hence, option (d) is the correct choice.
11. An antibiotic resistance gene in a vector usually helps in the selection of:
a. Competent bacterial cells
b. Transformed bacterial cells
c. Recombinant bacterial cells
d. None of the above
Ans: Antibiotic resistance genes in a vector usually help in the selection of transformed cells i.e, they act as a selectable marker. Selectable markers help in identifying the transformed cells. Generally, antibiotics such as Chloramphenicol, tetracycline, ampicillin are considered useful selectable markers.
Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
12. Significance of ‘heat shock’ method in bacterial transformation is to facilitate:
a. Binding of DNA to the cell wall
b. Uptake of DNA through membrane transport proteins
c. Uptake of DNA through transient pores in the bacterial cell wall
d. Expression of antibiotic resistance gene
Ans: Heat shock method in bacterial transformation is to facilitate uptake of DNA through transient pores in the bacterial cell wall.
In this method presence of bivalent cation like Ca+2 creates transient pores in the cell wall allowing the uptake of foreign DNA from the surrounding.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
13. The role of DNA ligase in the construction of a recombinant DNA molecule is:
a. Formation of phosphodiester bond between two DNA fragments
b. Formation of hydrogen bonds between sticky ends of DNA fragments
c. Ligation of all purine and pyrimidine bases
d. None of the above
Ans: DNA ligase is an enzyme that facilitates the joining of sticky ends of two DNA strands by the formation of phosphodiester bonds.
Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
14. Which of the following bacteria is not a source of restriction endonuclease?
a. Haemophilusinfluenzae
b. Escherichia coli
c. Entamoeba coli
d. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
Ans: Entamoeba coli is a protozoa. Therefore, it’s not a source of restriction endonuclease.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
15. Which of the following steps are catalysed by Taq DNA polymerase in a PCR reaction?
a. Denaturation of template DNA
b. Annealing of primers to template DNA
c. Extension of primer end on the template DNA
d. All of the above
Ans: Extension of primer end on the template DNA catalysed by Taq DNA polymerase in a PCR reaction.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
16. A bacterial cell was transformed with a recombinant DNA molecule that was generated using a human gene. However, the transformed cells did not produce the desired protein. Reasons could be:
a. Human gene may have intron which bacteria cannot process
b. Amino acid codons for humans and bacteria are different
c. Human protein is formed but degraded by bacteria
d. All of the above
Ans: Bacterial cell was transformed with a recombinant DNA molecule that was generated using a human gene. However, the transformed cells did not produce the desired protein because the human gene may have an intron that bacteria cannot process. Any nucleotide sequence in a gene is removed by splicing during the maturation of RNA which is called an intron. Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
17. Which of the following should be chosen for best yield if one were to produce a recombinant protein in large amounts?
a. Laboratory flask of largest capacity
b. A stirred-tank bioreactor without in-lets and out-lets
c. A continuous culture system
d. Any of the above
Ans: To grow something it requires a growth media and for producing recombinant protein in large amounts continuous culture system is a must.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
18. Who among the following was awarded the Nobel Prize for the development of PCR technique?
a. Herbert Boyer
b. HargovindKhurana
c. Kary Mullis
d. Arthur Kornberg
Ans: Karry Mullis invented a technique called Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) by which large amounts of DNA can be formed from small amounts.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
19. Which of the following statements does not hold true for restriction enzyme?
a. It recognises a palindromic nucleotide sequence
b. It is an endonuclease
c. It is isolated from viruses
d. It can produce the same kind of sticky ends in different DNA molecules
Ans: Restriction enzymes are isolated from bacteria, not from viruses.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
Very Short Answer Type Questions: class 12 biology biotechnology principles and processes
1. How is the copy number of the plasmid vector related to the yield of the recombinant protein?
Ans: Higher number of plasmid vectors results in the yield of a higher number of recombinant proteins.
2. Would you choose an exonuclease while producing a recombinant DNA molecule?
Ans: No, I would not choose exonuclease while producing a recombinant DNA molecule because it removes nucleotides from the ends of the DNA, and thus it cannot help in producing circular DNA.
3. What does H in ‘d’ and ‘III’ refer to in the enzyme HindIII?
Ans: No, I would not choose exonuclease while producing a recombinant DNA molecule because it removes nucleotides from the ends of the DNA, and thus it cannot help in producing circular DNA.
4. Restriction enzymes should not have more than one site of action in the cloning site of a vector. Comment.
Ans: Restriction enzymes should not have more than one site of action in the cloning site of a vector because the presence of more than one recognition site will create many fragments of DNA which will complicate the process.
5. What does ‘competent’ refer to in competent cells used in transformation experiments?
Ans: DNA is a hydrophilic molecule and so it cannot pass through the cell membrane thus the cell is made competent (pores are created) by treating suitable divalent ions. As a result, bacterial cells take up the DNA through the pores in the cell wall.
6. What is the significance of adding proteases at the time of isolation of genetic material (DNA).
Ans: The significance of adding proteases is that it helps in removing protein during the process of obtaining pure DNA
7. While doing a PCR, ‘denaturation’ step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
Ans: During PCR, if denaturation is missed then primers will not join the template and this will halt the further process i.e., no extension, no amplification and at the end, large numbers of DNA cannot be made.
8. Name a recombinant vaccine that is currently being used in a vaccination program.
Ans: Hepatitis B vaccine is currently being used in a vaccination program.
9. Do biomolecules (DNA, protein) exhibit biological activity in anhydrous conditions?
Ans: Biomolecules such as DNA, protein do not exhibit biological activity in anhydrous conditions as they may get damaged under anhydrous conditions and proteins get denatured.
10. What modification is done on the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to convert it into a cloning vector?
Ans: Agrobacterium tumefaciens has the ability to infect plant cells and then transfer a DNA sequence (Ti plasmid) and cause a crown gall disease.
This plasmid vector is disarmed and then used as a cloning vector for delivering genes of interest to plants and animals.
Short Answer Type Questions: class 12 biology biotechnology principles and processes
1. What is meant by gene cloning?
Ans: Gene cloning is a process by which multiple copies of a specific gene can be produced. This is done by:
Selecting specific gene
The selected gene is ligated to a vector.
Recombinant DNA or rDNA is produced.
This rDNA is now transformed into a bacterial cell.
As bacteria reproduce, their colony increases and each progeny will have that rDNA.
Thus, the number of copies of genes increases.
2. Both a wine maker and a molecular biologist who had developed a recombinant vaccine claim to be biotechnologists. Who in your opinion is correct?
Ans: Biotechnology is a branch of science in which living organisms are used to produce products for humankind. So, yes, both winemakers and molecular biologists are biotechnologists.
3. A recombinant DNA molecule was created by ligating a gene to a plasmid vector. By mistake, an exonuclease was added to the tube containing the recombinant DNA. How does this affect the next step in the experiment i.e. bacterial transformation?
Ans: When a DNA molecule is created by ligating a gene to a plasmid vector then it becomes a circular DNA, if by mistake exonuclease is added to the tube it will not affect the process because now DNA is not having a free end and thus exonuclease will not get a substrate to show its action.
4. Restriction enzymes that are used in the construction of recombinant DNA are endonucleases which cut the DNA at ‘specific-recognition sequence’. What would be the disadvantage if they do not cut the DNA at specific-recognition sequence?
Ans: Restriction enzymes that are used in the construction of recombinant DNA are endonucleases which cut the DNA at ‘specific-recognition sequence’ because specific-recognition sequence in the DNA provide sticky ends at which recombination of genes takes place which further leads to replication of selected gene and if endonucleases fail to cut the DNA at specific-recognition sequence the recombination will fail to occur.
5. A plasmid DNA and a linear DNA (both are of the same size) have one site for a restriction endonuclease. When cut and separated on agarose gel electrophoresis, plasmid shows one DNA band while linear DNA shows two fragments. Explain.
Ans: A plasmid DNA and linear DNA have one site for a restriction endonuclease, when cut and separated on agarose gel then circular DNA opens up to resemble a single linear DNA and linear DNA divides into two fragments after cleavage. Thus, circular DNA shows one band and linear DNA shows two bands.
6. How does one visualise DNA on an agarose gel?
Ans: While doing gel electrophoresis then the gel is added with a compound called Ethidium Bromide which stains the DNA so when DNA fragments are separated then it is put under UV radiation, fluorescence gives orange light. Thus, DNA fragments appear as orange bands in the presence of Ethidium Bromide and UV light.
7. A plasmid without a selectable marker was chosen as a vector for cloning a gene. How does this affect the experiment?
Ans: The function of the selectable marker is to identify and eliminate non-transformant DNA and selectively allow the growth of transformants. So, in the absence of a selectable marker, it is not possible to segregate transformants and non-transformants.
8. A mixture of fragmented DNA was electrophoresed in an agarose gel. After staining the gel with ethidium bromide, no DNA bands were observed. What could be the reason?
Ans: A mixture of fragmented DNA was electrophoresed in an agarose gel. After staining the gel with ethidium bromide, no DNA bands were observed the following possible reasons can be behind this:
- Maybe DNA gets contaminated because of the accidental addition of nuclease enzymes.
- Maybe electrodes are put on the wrong side i.e., anode towards the loading well. As DNA is negatively charged, it moves back towards the anode.
- Maybe the quantity of ethidium bromide was not sufficient.
9. Describe the role of CaCl2 in the preparation of competent cells?
Ans: CaCl2 provides the divalent ion i.e., Ca2+ which creates transient pores on the bacterial cell wall which then facilitates the entry of foreign DNA in the bacterial cell. So, because of divalent ions, the cell becomes competent and it increases the efficiency of uptake of DNA through the pores.
10. What would happen when one grows a recombinant bacterium in a bioreactor but forgets to add an antibiotic to the medium in which the recombinant is growing?
Ans: If antibiotics are not added in the growing medium then the bacteria do not have any pressure to create antibiotic-resistant genes as they are easily surviving and as a result, desirable genes would not produce.
11. Identify and explain steps ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ in the PCR diagram given below.
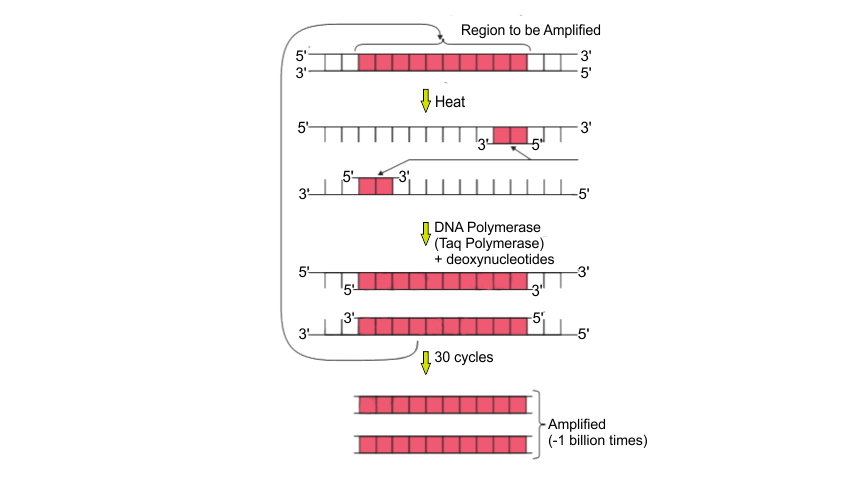
Ans:
A: Denaturation- Strands of DNA are separated into single strands by breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs.
B: Annealing- It is a heat treatment process of DNA in which a cycle of reaction of heating and cooling is done.
C: Extension- By using DNA polymerase copy of the DNA strand is made.
12. Name the regions marked A, B and C.
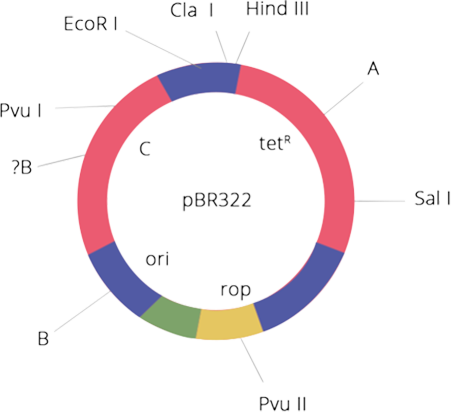
Ans:
A- shows tetracycline resistance site
B- shows restriction site Pst I
C- shows ampicillin resistance site
Long Answer Type Questions: class 12 biology biotechnology principles and processes
1. For a, visualize-specific recognition selection of recombinants, insertional inactivation of the antibiotic marker has been superseded by insertional inactivation of a marker gene coding for a chromogenic substrate. Give reasons.
Ans: Selecting recombinants by inactivating antibiotics is a difficult process because it requires plating on two different antibiotic plates simultaneously. To simplify this, researchers developed alternative selectable markers that differentiate recombinants from non-recombinants based on their ability to produce color in the presence of a chromogenic substrate. The enzyme beta-galactosidase becomes inactivated through a process known as insertional inactivation. When the chromogenic substrate is present, bacteria with plasmids lacking an insert form blue colonies. In contrast, the presence of an insert leads to the inactivation of alpha-galactosidase, resulting in colorless colonies that are identified as recombinant colonies.
2. Describe the role of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in transforming a plant cell.
Ans: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, a pathogen of several dicot plants, inserts a piece of DNA called ‘T-DNA’ into plant cells, transforming normal cells into tumor cells to produce chemicals required by the pathogen. The tumor-inducing Ti plasmid has been modified into a cloning vector that is no longer pathogenic to plants but still uses the same mechanism to deliver genes of interest into various plants.”
This version focuses on the active role of Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the modified Ti plasmid in the process.
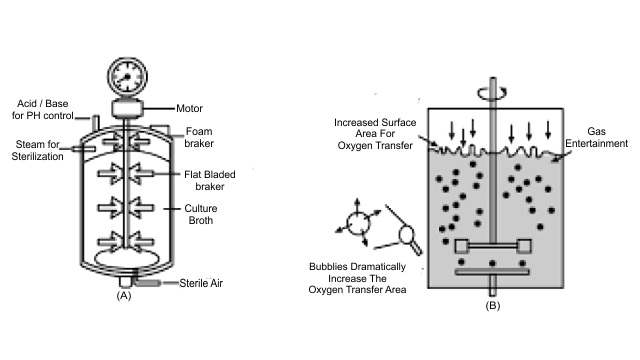
3. Illustrate the design of a bioreactor. Highlight the difference between a flask in your laboratory and a bioreactor which allows cells to grow in a continuous culture system.
Ans:
Bioreactors are large vessels that convert raw materials into specific products through biological processes. The most common type is the stirring bioreactor, which is cylindrical with a curved base to enhance material mixing. It includes an agitator system, oxygen delivery system, foam control system, and temperature control system, along with a sampling port for periodic product collection.
In contrast, laboratory flasks are unsuitable for large-scale rDNA production and continuous culture growth.
NCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Science
Students must practise these additional questions for their own benefits, the ncert exemplar are curated by the best subject-matter experts to boost your knowledge on the presented topic. Students can easily access the ncert exemplar for class 12 science by visiting our website SimplyAcad and solve all the questions listed to secure maximum marks.
Here are some other NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology:
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 1 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 6 |
|---|---|
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 2 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 7 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 3 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 8 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 4 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 9 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 5 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 10 |
latest video
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua




