NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production
NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9
NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 helps students deepen their understanding of Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production. This exemplar from SimplyAcad covers all the key areas of Chapter 9 in the biology textbook. It includes various types of questions—MCQs, very short, short, and long answers—designed by subject experts. These questions help students get familiar with different exam patterns, making it easier to perform well in their 12th board exams.
Students can easily access the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology below. Additionally, there are detailed exemplars available for other Class 12 Science chapters. SimplyAcad has made your preparation simpler and more effective.
Access the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Exemplar class 12 biology Chapter 9 MCQ Questions
MCQ Questions
1. The chances of contracting bird flu from a properly cooked (above 100°C) chicken and egg are:
a. very high
b. high
c. moderate
d. negligible
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer.
2. A group of animals which are related by descent and share many similarities are referred to as:
a. breed
b. race
c. variety
d. species
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
3. Inbreeding is carried out in animal husbandry because it:
a. increases vigour
b. improves the breed
c. increases heterozygosity
d. increases homozygosity
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer.
4. Sonalika and Kalyan Sona are varieties of:
a. wheat
b. rice
c. millet
d. tobacco
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
5. Which one of the following is not a fungal disease?
a. Rust of wheat
b. Smut of Bajra
c. Black rot of crucifers
d. Red rot of sugarcane
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
6. In virus-infected plants, the meristematic tissues in both apical and axillary buds are free of the virus because:
a. the dividing cells are virus-resistant
b. meristems have anti-viral compounds
c. the cell division of meristems is faster than the rate of viral multiplication
d. Viruses cannot multiply within the meristem cell (s).
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
7. Several South Indian states raise 2-3 crops of rice annually. The agronomic feature that makes this possible is because of
a. shorter rice plant
b. better irrigation facilities
c. early yielding rice variety
d. disease-resistant rice variety
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
8. Which one of the following combinations would a sugarcane farmer look for in the sugarcane crop?
a. Thick stem, long internodes, high sugar content and disease-resistant
b. Thick stem, high sugar content and profuse flowering
c. Thick stem, short internodes, high sugar content, disease-resistant
d. Thick stem, low sugar, content, disease-resistant
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
9. Fungicides and antibiotics are chemicals that:
a. enhance yield and disease resistance
b. kill pathogenic fungi and bacteria, respectively
c. kill all pathogenic microbes
d. kill pathogenic bacteria and fungi, respectively
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
10. Use of certain chemicals and radiation to change the base sequences of genes of crop plants are termed:
a. recombinant DNA technology
b. transgenic mechanism
c. mutation breeding
d. gene therapy.
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
11. The scientific process by which crop plants are enriched with certain desirable nutrients are called:
a. crop protection
b. breeding
c. bio-fortification
d. bio-remediation.
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
12. The term ‘totipotency’ refers to the capacity of a:
a. cell to generate a whole plant
b. bud to generate a whole plant
c. seed to germinate
d. cell to enlarge in size
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
13. Given below are a few statements regarding somatic hybridization. Choose the correct statements.
(i) protoplasts of different cells of the same plant are fused
(ii) protoplasts from cells of different species can be fused
(iii) treatment of cells with cellulase and pectinase is mandatory
(iv) the hybrid protoplast contains characters of only one parental protoplast.
a. (i) and (iii)
b. (i) and (ii)
c. (i) and (iv)
d. (ii) and (iii)
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer.
14. An explant is:
a. dead plant
b. part of the plant
c. part of the plant used in tissue culture
d. part of the plant that expresses a specific gene.
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
15. The biggest constraint of plant breeding is:
a. availability of desirable genes in the crop and its wild relatives
b. infrastructure
c. trained manpower
d. transfer of genes from unrelated sources.
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
16. Lysine and tryptophan are:
a. proteins
b. non-essential amino acids
c. essential amino acids
d. aromatic amino acids.
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
17. Micro-propagation is:
a. propagation of microbes in vitro
b. propagation of plants in vitro
c. propagation of cells in vitro
d. growing plants on a smaller scale.
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
18. Protoplast is:
a. another name for protoplasm
b. an animal cell
c. a plant cell without a cell wall
d. a plant cell.
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
19. To isolate protoplast, one needs:
a. pectinase
b. cellulase
c. both pectinase and cellulase
d. chitinase.
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
20. Which one of the following is a marine fish:
a. Rohu
b. Hilsa
c. Catla
d. Common Carp.
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
21. Which one of the following products of apiculture is used in cosmetics and polishes:
a. honey
b. propolis
c. wax
d. Royal jelly
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
22. More than 70 per cent of the livestock population is found in:
a. Denmark
b. India
c. China
d. India and China.
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer.
23. The agriculture sector of India employs about:
a. 50 per cent of the population
b. 70 per cent of the population
c. 30 per cent of the population
d. 60 per cent of the population.
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer.
24. 33 per cent of India’s Gross Domestic Product comes from
a. Industry
b. Agriculture
c. Export
d. Small-scale cottage industries.
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
25. A collection of all the alleles of all the genes of a crop plant is called:
a. germplasm collection
b. protoplasm collection
c. herbarium
d. somaclonal collection.
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
Exemplar class 12 biology Chapter 9 Very Short Answer Type Questions
1. Millions of chickens were killed in West Bengal, Assam, Orissa, and Maharashtra recently. What was the reason?
Solution: Chickens were culled to prevent the spread of bird flu (H5N1 virus) to other areas.
2. Can gamma rays used for crop improvement programs prove to be harmful to health?
Solution: Gamma rays induce mutations in crops, but the crops with beneficial mutations are selected for further growth. Since humans are not directly exposed to these rays, they are not harmful to health.
3. In animal husbandry, if two closely related animals are mated for a few generations, it results in loss of fertility and vigor. Why is this so?
Solution: Continued inbreeding leads to inbreeding depression, resulting in the accumulation of recessive genes, which causes a loss of fertility and vigor.
4. In the area of plant breeding, it is important not only to preserve the seeds of the variety being cultivated but also to preserve all its wild relatives. Explain with a suitable example.
Solution: Wild varieties of cultivated plants, though low-yielding, possess resistant genes that can be introduced into high-yielding plants. For example, wild rice varieties may carry genes for disease resistance.
5. Name a man-made cereal? Trace how it was developed and where it is used.
Solution: Triticale is a man-made cereal, developed by crossing rye with wheat. It is mainly used as animal fodder.
6. Fill in the blanks
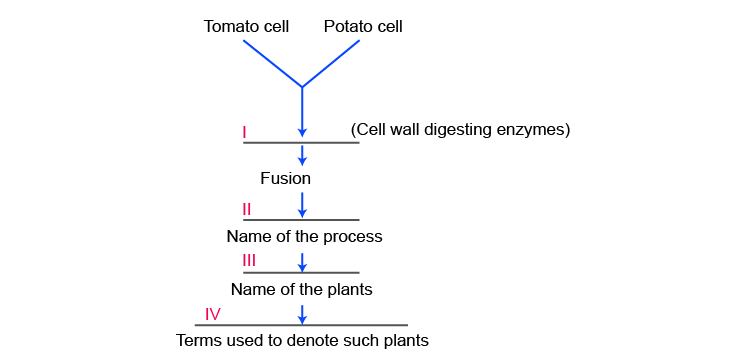
Solution: I: Cellulases catalyze
II: Somatic hybridization
III: Pomato/Topato
IV: Somatic hybrid
7. A few statements are given below, followed by a set of terms in a box. Pick the correct term and write it against the appropriate statement:
a. Mating of closely related individuals within the same breed
b. Mating of animals of the same breed but having no common ancestors on either side for 4-6 generations
c. Mating of animals of two different species
d. Breeding of animals belonging to different breeds
(i) Crossbreeding, (ii) Inter-specific hybridization, (iii) Outbreeding, (iv) Outcrossing, (v) Inbreeding
Solution: a. Inbreeding
b. Outcrossing
c. Inter-specific breeding
d. Crossbreeding
8. What is meant by ‘hidden hunger’?
Solution: Hidden hunger refers to the deficiency of essential nutrients in the body without visible symptoms.
9. Why are plants obtained by protoplast culture called somatic hybrids?
Solution: Plants obtained by protoplast culture are called somatic hybrids because they are formed by the fusion of protoplasts from two different plant varieties, each contributing desirable traits.
10. What is protoplast fusion?
Solution: Protoplast fusion involves the fusion of protoplasts (cells without cell walls) from different plant species under laboratory conditions to create a hybrid with desirable traits.
11. Why is it easier to culture meristems compared to permanent tissues?
Solution: Meristems can divide and differentiate into a new plant, whereas permanent tissues have lost their ability to divide.
12. Why are proteins synthesized from Spirulina called single-cell proteins?
Solution: Spirulina produces a large amount of protein within a single cell, making it a rich source of single-cell protein.
13. A person who is allergic to pulses was advised to take a capsule of Spirulina daily. Give the reasons for the advice.
Solution: Spirulina is rich in protein, making it a suitable alternative for someone allergic to pulses.
14. What is aquaculture? Give an example of an animal that can be multiplied by aquaculture.
Solution: Aquaculture is the farming of aquatic plants and animals for economic use. An example of an animal that can be multiplied by aquaculture is fish.
15. What are the duties of a veterinary doctor in the management of a poultry farm?
Solution: A veterinary doctor monitors the health of the animals, provides regular checkups, administers vaccinations, and ensures the quality of meat and eggs.
16. Would it be wrong to call plants obtained through micro-propagation as ‘clones’? Comment.
Solution: No, it would not be wrong because plants obtained through micro-propagation are genetically identical to the parent plant, making them clones.
17. How is a somatic hybrid different from a hybrid?
Solution: A somatic hybrid is formed by the fusion of any two cells, whereas a hybrid is produced by the fusion of two different varieties or related species.
18. What is emasculation? Why and when is it done?
Solution: Emasculation is the removal of stamens (male reproductive parts) from a bisexual flower to prevent self-pollination. It is done before the flower matures to ensure cross-pollination.
19. Discuss the two main limitations of a plant hybridization program.
Solution:
- Availability of desirable traits.
- The possibility of undesirable traits being linked to desirable ones.
20. Interspecific crosses are rare in nature and intergeneric crosses are almost unknown. Why?
Solution: Interspecific crosses result in infertile progeny, making them rare in nature. Intergeneric crosses are nearly impossible because the species involved are too distantly related.
21. Differentiate between pisciculture and aquaculture.
Solution: Pisciculture is the cultivation of fish, while aquaculture involves the cultivation of all aquatic plants and animals.
22. Give two important contributions of Dr. M. S. Swaminathan.
Solution:
- Dr. M. S. Swaminathan is known as the ‘Father of the Green Revolution’ in India and developed high-yielding varieties of wheat.
- He advocated for sustainable development in India.
23. The term ‘desirable trait’ can mean different things for different plants. Justify the statement with suitable examples.
Solution: A trait like tallness may be desirable for one plant (e.g., for timber) but undesirable for another (e.g., for crops in high-wind areas). The desired trait varies based on the plant’s use and environment.
Exemplar class 12 biology Chapter 9 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. You are planning to set up a Dairy Farm. Describe the various aspects you would consider before you start the venture.
Solution:
First and foremost a proper cattle management is necessary where light and air should be available. Then, the availability of food on the farm is considered. The time and amount of food given to the cattle are taken into consideration. It is important to have an arrangement of health care to look after the cattle and also to do the treatment of sick animals.
2. It is said that diseases are spreading faster due to globalization and the increased movement of people. Justify the statement by taking the example of the H5N1 virus.
Solution:
Migrating from one place to another is an important cause of globalization. So the chance of the rapid spreading of infectious diseases is more. The virus even can move from human to human; hence, it is transferred to healthy individuals at a very fast pace. Bird flu can transmit from organism to organism.
3. Explain the concept of the Blue Revolution.
Solution:
The blue revolution is related to aquatic plants and animals. There was a wide increase in the practice of aquaculture, to increase production. The blue revolution resulted in a major increase in the aquatic organisms and their products.
4. A farmer was facing the problem of low yield from his farm. He was advised to keep a beehive in the vicinity. Why? How would the beehive help in enhancing yield?
Solution:
A beehive would have a large number of honey bees. The honey bee is the major pollinator of many plants. Thus pollination increases the seed production. This enhances the rate of pollination and increases the crop of plants.
5. Lifestyle diseases are increasing alarmingly in India. We are also dealing with large-scale malnutrition in the population. Is there any method by which we can address both of these problems together?
Solution:
Biofortification can be used to address both problems. It is a technique of breeding crops with higher levels of nutrients example vitamins, minerals, proteins, fats etc. It improves food quality also.
6. How can we improve the success rate of fertilization during artificial insemination in animal husbandry programmes?
Solution:
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET) is used to improve the success rate of fertilization during artificial insemination in animal husbandry.
7. What is meant by germplasm collection? What are its benefits?
Solution:
Germplasm collection is nothing but the collection of genes. The entire collection of plants or seeds having all the diverse alleles for all genes in a given crop is done. The benefit of this collection is to maintain diversity. The genes are collected and stored and hence then can be used for future needs.
8. Name the improved characteristics of wheat that helped India to achieve a green revolution.
Solution:
Semi-dwarf: The height of the improved plant was neither too short nor too long, hence being semi-dwarf.
High yield: The yield of the improved wheat was very high as compared to the previous times.
Early maturity: Early maturity of the plant was necessary for high production.
9. Suggest some of the features of plants that will prevent insect and pest infestation.
Solution:
Morphological features: Various plants have a certain hair-like structure in the stem and other parts of the plants, these features prevent insect pests and Biochemical features which provide resistance to the plants.
10. It is easier to culture plant cells in vitro as compared to animal cells. Why?
Solution:
Dedifferentiation is the ability of the cells to lose as well as reverse the ability of differentiation. The plants have the ability to dedifferentiation and become meristematic again. Animals do not have this ability.
11. The culture medium (nutrient medium) can be referred to as a ‘highly enriched laboratory soil. Justify the statement.
Solution:
A culture medium is defined as an artificially prepared growth medium. This medium has various nutrients, chemicals, growth regulators, food supplements that are needed for the proper growth and nourishment of the growing cell. The natural occurring medium is the soil where all the minerals, nutrients, decomposers, water and all the things required for the growth of organisms are present.
12. Is there any relationship between dedifferentiation and the higher degree of success achieved in plant tissue culture experiments?
Solution:
Dedifferentiation of plant cells is very important in plant tissue culture, as any kind of tissue can be produced from differentiated cells. The plant cells can reverse the process of differentiation.
13. “Give me a living cell of any plant, and I will give you a thousand plants of the same type” Is this only a slogan, or is it scientifically possible? Write your comments and justify them.
Solution:
Tissue culture is the method through which we can produce thousands of plants of the same type by a single cell. The growth takes place under sterile conditions in a special nutrient medium which contains a carbon source, inorganic salts, amino acids, vitamins and other growth regulators.
14. What is the difference between a breed and a species? Give an example for each category.
Solution:
A breed is a group of animals having a similar appearance, behaviour and other characteristics. An example is a breed of dog Afghan shepherd, Akbash etc. A species is a group of plants and animals that live together and are capable of reproduction to produce offspring. An example is the different species of the genus Homo.
15. Plants raised through tissue cultures are clones of the ‘parent’ plant. Discuss the utility of these plants.
Solution:
Tissue culture is the method through which we can produce thousands of plants of the same type by a single cell. The plants that are produced by tissue culture are used to produce thousand and more exact copies of an economically important plant.
16. Discuss the importance of testing of new plant varieties in a geographically vast country like India.
Solution:
The new plant varieties are grown in research fields to check the quality and quantity of the product. To check whether the variety is affected by disease or not, the testing is done and also to ensure the high and nutritious yield of the plant.
17. Define the term ‘stress’ for plants. Discuss briefly the two types of stress encountered by plants.
Solution:
Stress is any negative impact on the plant that is caused due to any factor whether biotic or abiotic. Stress affects the growth and development of the plant. The two types of stress encountered by plants are water stress and salt stress.
18. Discuss natural selection and artificial selection. What are the implications of the latter on the process of evolution?
Solution:
Natural selection is the rule of nature and it occurs naturally. The organism that is best suited to the environment and changes and adapts with time is naturally selected by nature.
Artificial selection- It is an artificial way of selecting organisms and characters by the humans themselves
19. Discuss briefly how pure lines are created in animal husbandry.
Solution:
Pureline is a breed or strain of plants and animals that have homozygous alleles and have similar characteristics for various generations. It is created in animal husbandry by repeating inbreeding male and female animals of the same breed for 4-5 generations.
20. What are the physical barriers of a cell in the protoplast fusion experiment? How are the barriers overcome?
Solution:
The cell wall is the most and only physical barrier of a cell in the protoplast. This physical barrier is overcome by its breakdown. The breakdown of the cell wall is done by digesting the cell wall.
21. Give a few examples of biofortified crops. What benefits do they offer to society?
Solution:
Maize hybrid (It has twice the number of amino acids, lysine and tryptophan.)
Atlas 66, a wheat hybrid (It has high protein content.)
Iron-fortified rice (It has iron over five times more than the normal rice) etc are the examples for the biofortified crops.
Benefits:
1. They will have high nutrient quantity.
2. They can be used to control malnutrition and other lifestyle diseases also.
Exemplar class 12 biology Chapter 9 LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. You are a Botanist working in the area of plant breeding. Describe the various steps that you will undertake to release a new variety.
Solution:
The various steps undertaken while releasing a new variety are
1. Collection of variability: Variety of genes and characters are collected from all the wild variety present of the specific plant.
2. Evaluation and selection of parents: Parents are selected according to the desirable traits and characteristics.
3. Cross hybridisation among the selected parents: The two parents with desirable traits are crossed such that both the desirable trait now occurs in one plant. This is a time-consuming task
4. Selection and testing of superior recombinants: Select the superior hybrids that have the desirable characteristics of both the parents.
5. Testing, release and commercialisation of the new cultivars: To test the quality and evaluate the quantity of the product after selecting the superior hybrid, they are allowed to grow in the research field. Only that hybrid whose product is qualitatively and quantitatively good is released to grow economically
2. (a) The shift from grain to meat diets creates more demand for cereals. Why?
(b) A 250 kg cow produces 200 g of protein per day but 250 g of Methylophillusmethylotrophus can produce 25 tonnes of protein Name this emerging area of research. Explain its benefits.
Solution:
(a) The shift from grains to meat diets create more demands for cereals because humans consume meat which is obtained from animals such as goat, chicken, cow etc. These animals consume cereals for their nourishment and produce 1kg of meat.
(b) The name of this emerging area of research is Single Cell Protein. It is an alternate source of proteins for animal and human nutrition. They produce a large amount of protein in a short period. It is less time-consuming and high-yielding method.
3. What are the advantages of tissue culture methods over the conventional method of plant breeding in crop improvement programmes?
Solution:
1. Conventional breeding techniques failed to keep pace with the growing demands of the current time.
2. Tissue culture produces thousands of exact plant together in a short period
3. An explant or any part of the plant is selected and is grown in a test tube.
4. The growth takes place under sterile conditions in a special nutrient medium which contains a carbon source, inorganic salts, amino acids, vitamins and other growth regulators.
5. The tissue culture also helps in the recovery of the healthy plant from a diseased plant.
4. ‘Modern methods of breeding animals and plants can alleviate the global food shortage’. Comment on the statement and give suitable examples.
Solution:
1. MOET:
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET) is used to improve the success rate of fertilization during artificial insemination in animal husbandry. Here the cow is administered with certain hormones with FSH like activity.
2. SINGLE CELL PROTEIN:
Single-cell protein is used as the alternate source of proteins for animal and human nutrition. It is very
Advantageous as the microbes are grown in a very huge amount.
3. BIOFORTIFICATION:
Biofortification is a technique of breeding crops with higher levels of nutrients example vitamin, minerals, proteins, fats etc.
4. TISSUE CULTURE:
Tissue culture is the method through which we can produce thousands of plants of the same type by a single cell.
5. Does apiculture offer multiple advantages to farmers? List its advantages if it is located near a place of commercial flower cultivation.
Solution:
Apiculture is the maintenance of hives of honeybees for the production of honey. It is also known as beekeeping.
1. It provides honey and wax and other honey products. The farmers sell these and get extra money.
2. They are good pollinators and increase the rate of pollination.
3. A beehive would have a large number of honey bees. The honey bee is the major pollinator of many plants.
4. Good pollination results in the increase in seed production, ultimately increasing the crop of plants.
5. The pollination of the crops will take place at a good rate and helps farmers.
6. (a) Mutations are beneficial for plant breeding. Taking an example, justify the statement.
(b) Discuss briefly the technology that made us self-sufficient in food production.
Solution:
(a) The mutation is processed by which the genetic sequence of the plant can be altered. Mutations can occur naturally and it is induced too. In mung bean, resistance to yellow mosaic virus and powdery mildew were induced by mutations.
(b) The technology that has made us self-sufficient in food production is plant breeding. the best variety of plant with desirable traits is grown to release a variety of products.
7. Discuss how the property of plant cell totipotency has been utilised for plant propagation and improvement
Solution:
Tissue culture is the method through which we can produce thousands of plants of the same type by a single cell. This ability to develop the whole plant from a single cell is known as totipotency. Totipotency helps in the production of thousands of plants that are genetically similar. This large-scale production of plants is known as micro-propagation.
8. What are three options to increase food production? Discuss each giving the salient features, merits and demerits.
Solution:
(a) Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology is one way to increase food production.
(b) Tissue culture is another way that helps in the production of a large number of plants within a very short period with just a single cell.
c) Single-cell protein is an alternative source of protein obtained from microbes.
DEMERITS:
a. Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology is a high-cost method, and the success rate is low
b. There is a reduction of genetic diversity in the case of tissue culture
c. In single-cell proteins, their maintenance is a very costly process
NCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Science
Here are some other NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology:
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 1 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 12 |
|---|---|
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 2 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 13 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 3 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 14 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 4 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 15 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 5 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 biology Chapter 16 |
More Questions for Chapter 9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Q1: What is plant breeding, and why is it important?
A: Plant breeding improves plant varieties to increase yield, disease resistance, and adaptability. This process plays a crucial role in boosting food production to meet the demands of a growing population.
Q2: What are the steps in plant breeding?
A: The main steps in plant breeding include:
- Collecting genetic diversity.
- Selecting parents with desirable traits.
- Cross-breeding the selected parents.
- Choosing the best hybrids.
- Testing and releasing new varieties.
Q3: How does tissue culture boost food production?
A: Tissue culture quickly produces large numbers of disease-free, identical plants under sterile conditions, which leads to significant increases in food production.
Q4: What is biofortification, and how does it help?
A: Biofortification breeds crops to increase their nutritional value, like higher levels of vitamins and minerals. This process improves food quality, addressing malnutrition and enhancing food security.
Q5: What methods in animal husbandry boost food production?
A: Effective methods include:
- Selective breeding
- Artificial insemination
- Embryo transfer technology
- Better feeding practices
- Disease management
Q6: Why is genetic engineering important for food production?
A: Genetic engineering modifies the genes of plants and animals to introduce traits like pest resistance and improved nutrition, leading to higher yields and better-quality food.
Q7: How do single-cell proteins (SCP) contribute to food production?
A: Single-cell proteins (SCP), derived from microorganisms, provide a protein-rich food source, offering a sustainable and efficient way to produce protein.
Q8: How does organic farming support sustainable food production?
A: Organic farming uses natural methods like crop rotation and biological pest control, maintaining soil health and reducing pollution while producing safer, healthier food.
Q9: What role do apiculture and aquaculture play in food production?
A: Apiculture (beekeeping) supports crop pollination and honey production, while aquaculture (farming fish and aquatic organisms) offers a sustainable source of protein.
Q10: How does hybridization improve food production?
A: Hybridization crosses two different plants or animals to create offspring with the best traits from both, leading to higher yields, better quality, and greater resistance to diseases.
latest video
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua




