NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry
NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3
SimplyAcad has provided the NCERT exemplar class 12 chemistry Chapter 2 solutions below to help students learn all the chapters in a detailed manner. The exemplar will allow students to gain deep insights of all the sections and prepares you for the upcoming examination. Chemistry is an interesting subject which requires attention to minor details, hence, completing exemplars will be an effective way to increase your marks and confidence. The given exemplar contains MCQs of two different types, Short Answer Type Questions, and Matching Types questions, there are a total of 49 questions asked. Students can access the NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry, Chapter 3 Electrochemistry by scrolling below. Along with this, there are several NCERT exemplar for class 12 science of all the chapters provided on this platform.
Access the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry
I. Ncert exemplar class 12 chemistry Chapter 3 – Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
Question 1
Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode?
(i) Pt (s) H₂(g, 0.1 bar) H⁺ (aq., 1 M) Cu²⁺ (aq., 1 M) Cu
(ii) Pt (s) H₂(g, 1 bar) H⁺ (aq., 1 M) Cu²⁺ (aq., 2 M) Cu
(iii) Pt (s) H₂(g, 1 bar) H⁺ (aq., 1 M) Cu²⁺ (aq., 1 M) Cu
(iv) Pt (s) H₂(g, 1 bar) H⁺ (aq., 0.1 M) Cu²⁺ (aq., 1 M) Cu
Solution:
Option (iii) is the correct answer.
Question 2
Electrode potential for Mg electrode varies according to the equation
EMg²⁺/Mg = EᶱMg²⁺/Mg – 0.0591/2 log1/[Mg²⁺]. The graph of EMg²⁺/Mg vs log [Mg²⁺] is:
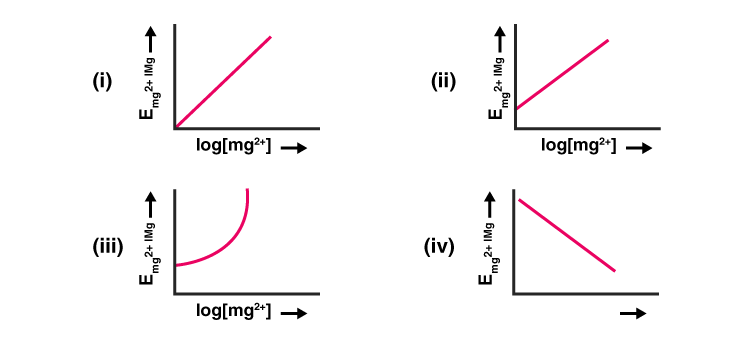
Solution:
Option (ii) is the correct answer.
Question 3
Which of the following statements is correct?
(i) ECell and ∆rG of cell reaction both are extensive properties.
(ii) ECell and ∆rG of cell reaction both are intensive properties.
(iii) ECell is an intensive property while ∆rG of cell reaction is an extensive property.
(iv) ECell is an extensive property while ∆rG of cell reaction is an intensive property.
Solution:
Option (iii) is the correct answer.
Question 4
The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called ___________.
(i) Cell potential
(ii) Cell emf
(iii) Potential difference
(iv) Cell voltage
Solution:
Option (ii) is the correct answer.
Question 5
Which of the following statements is not correct about an inert electrode in a cell?
(i) It does not participate in the cell reaction.
(ii) It provides surface either for oxidation or for the reduction reaction.
(iii) It provides a surface for conduction of electrons.
(iv) It provides a surface for a redox reaction.
Solution:
Option (iv) is the correct answer.
Question 6
An electrochemical cell can behave like an electrolytic cell when ____________.
(i) ECell = 0
(ii) ECell > EExt
(iii) EExt > ECell
(iv) ECell = EExt
Solution:
Option (iii) is the correct answer.
Question 7
Which of the statements about solutions of electrolytes is not correct?
(i) The conductivity of the solution depends upon the size of ions.
(ii) Conductivity depends upon the viscosity of the solution.
(iii) Conductivity does not depend upon solvation of ions present in solution.
(iv) The conductivity of the solution increases with temperature.
Solution:
Option (iii) is the correct answer.
Question 8
Using the data given below to find out the strongest reducing agent.
- EᶱCr₂O₇²⁻/Cr³⁺ = 1.33V
- EᶱMnO₄⁻/Mn²⁺ = 1.51V
- EᶱCl₂/Cl⁻ = 1.36V
- EᶱCr³⁺/Cr = -0.74V
(i) Cl⁻
(ii) Cr
(iii) Cr³⁺
(iv) Mn
Solution:
Option (ii) is the correct answer.
Question 9
Use the data given in Q.8 and find out which of the following is the strongest oxidizing agent.
(i) Cl⁻
(ii) Mn²⁺
(iii) MnO₄⁻
(iv) Cr³⁺
Solution:
Option (iii) is the correct answer.
Question 10
Using the data given in Q.8, find out in which option the order of reducing power is correct.
(i) Cr³⁺ < Cl⁻ < Mn²⁺ < Cr
(ii) Mn²⁺ < Cl⁻ < Cr³⁺ < Cr
(iii) Cr³⁺ < Cl⁻ < Cr₂O₇²⁻ < MnO₄⁻
(iv) Mn²⁺ < Cr³⁺ < Cl⁻ < Cr
Solution:
Option (ii) is the correct answer.
Question 11
Use the data given in Q.8 and find out the most stable ion in its reduced form.
(i) Cl⁻
(ii) Cr³⁺
(iii) Cr
(iv) Mn²⁺
Solution:
Option (iv) is the correct answer.
Question 12
Use the data of Q.8 and find out the most stable oxidized species.
(i) Cr³⁺
(ii) MnO₄⁻
(iii) Cr₂O₇²⁻
(iv) Mn²⁺
Solution:
Option (i) is the correct answer.
Question 13
The quantity of charge required to obtain one mole of aluminum from Al₂O₃ is ___________.
(i) 1F
(ii) 6F
(iii) 3F
(iv) 2F
Solution:
Option (iii) is the correct answer.
Question 14
The cell constant of a conductivity cell _____________.
(i) Changes with the change of electrolyte.
(ii) Changes with the change of concentration of electrolyte.
(iii) Changes with the temperature of the electrolyte.
(iv) Remains constant for a cell.
Solution:
Option (iv) is the correct answer.
Question 15
While charging the lead storage battery ______________.
(i) PbSO₄ anode is reduced to Pb.
(ii) PbSO₄ cathode is reduced to Pb.
(iii) PbSO₄ cathode is oxidized to Pb.
(iv) PbSO₄ anode is oxidized to PbO₂.
Solution:
Option (i) is the correct answer.
Question 16
˄₀m(NH₄OH) is equal to ______________.
(i) ˄₀m(NH₄OH) + ˄₀m(NH₄Cl) – ˄₀(HCl)
(ii) ˄₀m(NH₄Cl) + ˄₀m(NaOH) – ˄₀(NaCl)
(iii) ˄₀m(NH₄Cl) + ˄₀m(NaCl) – ˄₀(NaOH)
(iv) ˄₀m(NaOH) + ˄₀m(NaCl) – ˄₀(NH₄Cl)
Solution:
Option (ii) is the correct answer.
Question 17
In the electrolysis of an aqueous sodium chloride solution, which of the half-cell reactions will occur at the anode?
(i) Na⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Na(s); E°Cell = –2.71V
(ii) 2H₂O(l) → O₂(g) + 4H⁺(aq) + 4e⁻ : E°Cell = 1.23V
(iii) H⁺(aq) + e⁻ → 1/2H₂(g); E°Cell = 0.00V
(iv) Cl⁻(aq) → 1/2Cl₂(g) + e⁻ ; E°Cell = 1.36V
Solution:
Option (iv) is the correct answer.
II. Ncert exemplar class 12 chemistry Chapter 3 – Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
Note: In the following questions two or more than two options may be correct.
Question 18
The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu²⁺/Cu indicates that ____________.
(i) This redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H⁺/H₂ couple.
(ii) This redox couple is a stronger oxidizing agent than H⁺/H₂.
(iii) Cu can displace H₂ from acid.
(iv) Cu cannot displace H₂ from acid.
Solution:
Options (ii) and (iv) are the correct answers.
Question 19
E°Cell for some half-cell reactions are given below. Based on these, mark the correct answer.
(a) H⁺(aq) + e⁻ → 1/2H₂(g); E°Cell = 0.00V
(b) 2H₂O(l) → O₂(g) + 4H⁺(aq) + 4e⁻; E°Cell = 1.23V
(c) 2SO₄²⁻(aq) → S₂O₈²⁻(aq) + 2e⁻; E°Cell = 1.96V
(i) In dilute sulfuric acid solution, hydrogen will be reduced at the cathode.
(ii) In concentrated sulfuric acid solution, water will be oxidized at the anode.
(iii) In dilute sulfuric acid solution, water will be oxidized at the anode.
(iv) In dilute sulfuric acid solution, SO₄²⁻ ion will be oxidized to tetrathionate ion at the anode.
Solution:
Options (i) and (iii) are the correct answers.
Question 20
E°Cell = 1.1V for Daniel cell. Which of the following expressions are correct descriptions of the state of equilibrium in this cell?
(i) 1.1 = Kc
(ii) 2.303RT/2F logKc = 1.1
(iii) log Kc = 2.2/0.059
(iv) log Kc = 1.1
Solution:
Options (ii) and (iii) are the correct answers.
Question 21
Conductivity of an electrolytic solution depends on ____________.
(i) Nature of electrolyte.
(ii) The concentration of electrolyte.
(iii) Power of AC source.
(iv) Distance between the electrodes.
Solution:
Options (i) and (ii) are the correct answers.
Question 22
˄₀m(H₂O) is equal to ______________.
(i) ˄₀m(HCl) + ˄₀m(NaOH) – ˄₀m(NaCl)
(ii) ˄₀m(HNO₃) + ˄₀m(NaNO₃) – ˄₀m(NaOH)
(iii) ˄₀m(HNO₃) + ˄₀m(NaOH) – ˄₀m(NaNO₃)
(iv) ˄₀m(NH₄OH) + ˄₀m(HCl) – ˄₀m(NH₄Cl)
Solution:
Options (i) and (iii) are the correct answers.
Question 23
What will happen during the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of CuSO₄ by using platinum electrodes?
(i) Copper will deposit at the cathode.
(ii) Copper will deposit at the anode.
(iii) Oxygen will be released at the anode.
(iv) Copper will dissolve at the anode.
Solution:
Options (i) and (iii) are the correct answers.
Question 24
What will happen during the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of CuSO₄ in the presence of Cu electrodes?
(i) Copper will deposit at the cathode.
(ii) Copper will dissolve at the anode.
(iii) Oxygen will be released at the anode.
(iv) Copper will deposit at the anode.
Solution:
Options (i) and (ii) are the correct answers.
Question 25
Conductivity (κ) is equal to ____________.
(i) 1/R × l/A
(ii) G*/R
(iii) ˄m
(iv) l/A
Solution:
Options (i) and (ii) are the correct answers.
Question 26
Molar conductivity of an ionic solution depends on ___________.
(i) Temperature.
(ii) Distance between electrodes.
(iii) The concentration of electrolytes in solution.
(iv) The surface area of electrodes.
Solution:
Options (i) and (iii) are the correct answers.
Question 27
For the given cell, Mg | Mg²⁺ || Cu²⁺ | Cu:
(i) Mg is the cathode.
(ii) Cu is the cathode.
(iii) The cell reaction is Mg + Cu²⁺ → Mg²⁺ + Cu.
(iv) Cu is the oxidizing agent.
Solution:
Options (ii) and (iii) are the correct answers.
III. Ncert exemplar class 12 chemistry Chapter 3 – Short Answer Type
Question 28
Can absolute electrode potential of an electrode be measured?
Solution:
No, absolute electrode potential of an electrode cannot be measured. We can only measure the difference in electrode potential between two half-cells. We also measure electrode potential relative to a standard electrode, typically the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE).
Question 29
Can E°Cell or ΔrG° for a cell reaction ever be equal to zero?
Solution:
E°Cell or ΔrG° can never be equal to zero. The only standard electrode potential arbitrarily assigned the value zero is the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE). Since all other electrode potentials are measured relative to SHE, E°Cell can never be zero.
Question 30
Under what condition is ECell = 0 or ΔrG = 0?
Solution:
ECell = 0 or ΔrG = 0 occurs when the electrochemical cell has reached equilibrium. At equilibrium, the cell is fully discharged, no further reaction occurs, and the cell potential drops to zero. Therefore, no electrical work can be done by the cell.
Question 31
What does the negative sign in the expression E°Zn²⁺/Zn = -0.76V mean?
Solution:
The negative value indicates that the reduction of Zn²⁺ to Zn is less favorable than the reduction of H⁺ to H₂ (which is set as zero in the Standard Hydrogen Electrode). This means that Zn is more likely to oxidize (lose electrons) rather than reduce, making it a stronger reducing agent.
Question 32
Aqueous copper sulfate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolyzed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells. Will the mass of copper and silver deposited on the cathode be the same or different? Explain your answer.
Solution:
The mass of copper and silver deposited on the cathode will be different. This is because the equivalent mass (molar mass divided by the valency) of copper and silver are different, leading to different amounts of deposition. The deposition is calculated using Faraday’s laws of electrolysis:
Question 33
Depict the galvanic cell in which the cell reaction is Cu + 2Ag⁺ → 2Ag + Cu²⁺.
Solution:
Anode (Oxidation half-cell): Cu → Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻
Cathode (Reduction half-cell): 2Ag⁺ + 2e⁻ → 2Ag
Overall reaction: Cu + 2Ag⁺ → Cu²⁺ + 2Ag
The cell can be represented as:
Cu | Cu²⁺(aq, 1M) || Ag⁺(aq, 1M) | Ag
Question 34
Value of standard electrode potential for the oxidation of Cl⁻ ions is more positive than that of water, even then in the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, why is Cl⁻ oxidized at anode instead of water?
Solution:
The oxidation of water to oxygen is kinetically unfavorable and requires an overpotential (extra energy) to proceed. Because of this overpotential, Cl⁻ ions are preferentially oxidized at the anode during the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, even though the standard electrode potential suggests otherwise.
Question 35
What is electrode potential?
Solution:
Electrode potential is the potential difference developed between an electrode and its surrounding electrolyte due to the tendency of the electrode to gain or lose electrons. The standard electrode potential is always measured as the reduction potential relative to the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE).
Question 36
Consider the following diagram in which an electrochemical cell is coupled to an electrolytic cell. What will be the polarity of electrodes ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the electrolytic cell?
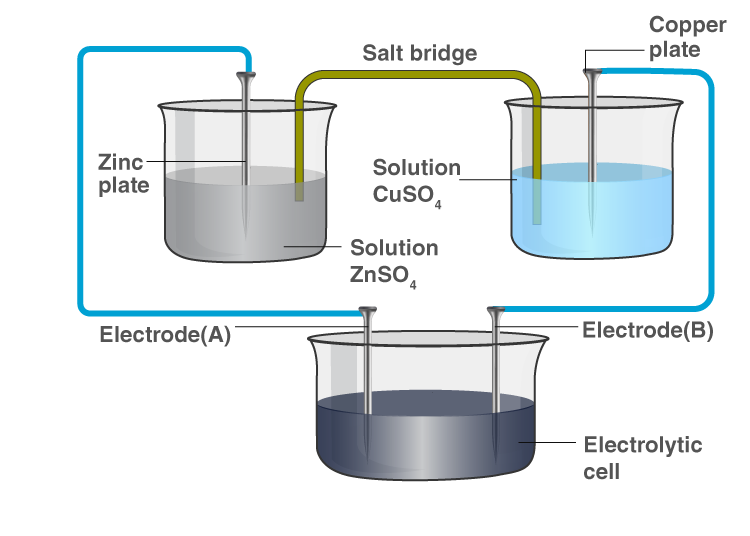
Solution:
In the electrochemical cell, zinc goes into solution as Zn²⁺, leaving behind electrons on Electrode A, making it negatively charged. Cu²⁺ from the solution deposits on Electrode B, making it positively charged.
- Electrode A polarity: Negative
- Electrode B polarity: Positive
Question 37
Why is alternating current used for measuring the resistance of an electrolytic solution?
Solution:
Alternating current is used to measure the resistance of an electrolytic solution because it prevents polarization of the electrodes, which would occur with direct current. Polarization affects the concentration of ions near the electrodes, altering the resistance. Alternating current keeps the ion concentration constant, providing an accurate measurement of resistance.
Question 38
A galvanic cell has an electrical potential of 1.1V. If an opposing potential of 1.1V is applied to this cell, what will happen to the cell reaction and current flowing through the cell?
Solution:
When an opposing potential of 1.1V (equal to the cell’s potential) is applied, the cell reaction will stop, and no current will flow through the cell. At this point, the cell is at equilibrium, and no chemical reaction takes place.
Question 39
How will the pH of brine (aq. NaCl solution) be affected when it is electrolyzed?
Solution:
During electrolysis of brine (NaCl solution):
- At the cathode: Water is reduced to produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻), increasing the pH.
- At the anode: Chloride ions (Cl⁻) are oxidized to chlorine gas, with no effect on pH.
The overall reaction results in the formation of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), which is a strong base. Thus, the pH of the solution will increase, making it more basic.
NCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Science
The NCERT exemplars are an effective study material for scoring higher marks in the examination paper. Students must practise these additional questions for their own benefits, as these are curated by the best subject-matter experts to boost both knowledge and confidence. Students can easily access the ncert exemplar for class 12 science by visiting our website SimplyAcad and solve all the questions listed to secure maximum marks.
Here are some other NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry:
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 1 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 7 |
|---|---|
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 2 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 8 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 4 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 9 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 5 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 10 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 6 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 11 |
latest video
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua




