NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6: General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements
NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6
NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chemistry Chapter 6 is an effective study material to boost your knowledge on the various sections of a chapter. Students can rely on this provided exemplar solutions of Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Element to solve questions and become more familiar with it. Our subject matter experts at SimplyAcad have made sure to convey all the information and minute details precisely to students for effective learning.
There are two types of MCQs based, short answer type, matching type and assertion and reason type answer questions which ensure that students cover every bit of the section. This will raise confidence in them and prepare them for the upcoming 12th board examination. Along with this, there are several NCERT exemplar for class 12 science of all the chapters provided on this platform.
Access the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Element
I. NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 – Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
1. In the extraction of chlorine by electrolysis of brine ____________.
(i) oxidation of Cl– ion to chlorine gas occurs.
(ii) reduction of Cl– ion to chlorine gas occurs.
(iii) For the overall reaction, ∆Gᶱ has a negative value.
(iv) a displacement reaction takes place.
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
2. When copper ore is mixed with silica, in a reverberatory furnace copper matte
is produced. The copper matte contains ____________.
(i) sulphides of copper (II) and iron (II)
(ii) sulphides of copper (II) and iron (III)
(iii) sulphides of copper (I) and iron (II)
(iv) sulphides of copper (I) and iron (III)Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
3. Which of the following reactions is an example of autoreduction?
(i) Fe3O4 + 4CO → 3Fe + 4CO2
(ii) Cu2O + C → 2Cu + CO
(iii) Cu2+ (aq) + Fe (s) → Cu (s) + Fe2+ (aq)
(iv) Cu2O + 1/2Cu2S → 3Cu + 1/2SO2
Solution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
4. A number of elements are available in earth’s crust but most abundant
elements are ____________.
(i) Al and Fe
(ii) Al and Cu
(iii) Fe and Cu
(iv) Cu and Ag
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
5. Zone refining is based on the principle that ___________.
(i) impurities of low boiling metals can be separated by distillation.
(ii) impurities are more soluble in molten metal than in solid metal.
(iii) different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an absorbent.
(iv) vapours of the volatile compound can be decomposed in pure metal.
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
6. In the extraction of copper from its sulphide ore, the metal is formed by the
reduction of Cu2O with
(i) FeS
(ii) CO
(iii) Cu2S
(iv) SO2
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
7. Brine is electrolysed by using inert electrodes. The reaction at anode is ________.
(i) Cl–(aq.) →1/2Cl2 (g) + e– ; E°cell = 1.36V
(ii) 2H2O(l) → O2(g0 + 4H+ + 4e- ; E°cell = 1.23V
(iii) Na+(aq) + e- → Na(s) ; E°cell = 2.71V
(iv) H+(aq) + e- → 1/2H2(g) ; E°cell = 0.00V
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
8. In the metallurgy of aluminium ________________.
(i) Al3+ is oxidised to Al (s).
(ii) graphite anode is oxidised to carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
(iii) the oxidation state of oxygen changes in the reaction at the anode.
(iv) the oxidation state of oxygen changes in the overall reaction involved in the process
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
9. Electrolytic refining is used to purify which of the following metals?
(i) Cu and Zn
(ii) Ge and Si
(iii) Zr and Ti
(iv) Zn and Hg
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
10. Extraction of gold and silver involves leaching the metal with CN–ion. The metal is recovered by ________________.
(i) displacement of metal by some other metal from the complex ion.
(ii) roasting of the metal complex.
(iii) calcination followed by roasting.
(iv) thermal decomposition of the metal complex.
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
Note: Answer the questions 11-13 based on Fig. 6.1.
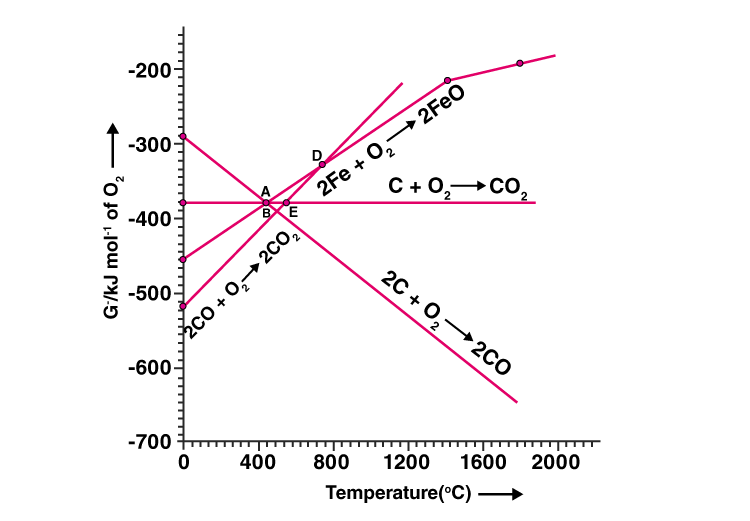
11. Choose the correct option of temperature at which carbon reduces FeO to iron
and produces CO.
(i) Below temperature at point A.
(ii) Approximately at the temperature corresponding to point A.
(iii) Above temperature at point A but below a temperature at point D.
(iv) Above temperature at point A.
Solution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
12. Below point ‘A’ FeO can ______________.
(i) be reduced by carbon monoxide only.
(ii) be reduced by both carbon monoxide and carbon.
(iii) be reduced by carbon only.
(iv) not be reduced by both carbon and carbon monoxide.
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer
13. For the reduction of FeO at the temperature corresponding to point D, which
of the following statements is correct?
(i) ∆G value for the overall reduction reaction with carbon monoxide is
zero.
(ii) ∆G value for the overall reduction reaction with a mixture of 1 mol carbon
and 1 mol oxygen is positive.
(iii) ∆G value for the overall reduction reaction with a mixture of 2 mol carbon
and 1 mol oxygen will be positive.
(iv) ∆G value for the overall reduction reaction with carbon monoxide is
negative.
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
II. NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 – Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
14. At the temperature corresponding to which of the points in Fig.6.1, FeO will
be reduced to Fe by coupling the reaction 2FeO → 2Fe + O2
with all of the
following reactions?
(a) C + O2 → CO2
(b) 2C + O2 → 2CO and (c) 2CO + O2 → 2 CO2
(i) Point A
(ii) Point B
(iii) Point D
(iv) Point ESolution:
Option (ii) and (iv) are the answers.
15. Which of the following option are correct?
(i) Cast iron is obtained by remelting pig iron with scrap iron and coke
using hot air blast.
(ii) In the extraction of silver, silver is extracted as cationic complex.
(iii) Nickel is purified by zone refining.
(iv) Zr and Ti are purified by van Arkel method
Solution:
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers.
16. In the extraction of aluminium by Hall-Heroult process, purified Al2O3
is mixed with CaF2 to
(i) lower the melting point of Al2O3
(ii) increase the conductivity of molten mixture.
(iii) reduce Al3+ into Al(s).
(iv) acts as a catalyst
Solution:
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers.
17. Which of the following statements is correct about the role of substances added
in the froth floatation process?
(i) Collectors enhance the non-wettability of the mineral particles.
(ii) Collectors enhance the wettability of gangue particles.
(iii) By using depressants in the process two sulphide ores can be separated.
(iv) Froth stabilisers decrease wettability of gangue.
Solution:
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers.
18. In the Froth Floatation process, zinc sulphide and lead sulphide can be
separated by ______________.
(i) using collectors.
(ii) adjusting the proportion of oil to water.
(iii) using depressant.
(iv) using froth stabilisers.
Solution:
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers.
19. Common impurities present in bauxite are ____________.
(i) CuO
(ii) ZnO
(iii) Fe2O3
(iv) SiO2
Solution:
Option (iii) and (iv) are the answers.
20. Which of the following ores are concentrated by froth flotation?
(i) Haematite
(ii) Galena
(iii) Copper pyrites
(iv) MagnetiteSolution:
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers.
21. Which of the following reactions occur during calcination?
(i) CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
(ii) 2FeS2 + 11/2 O2 → Fe2O3 + 4SO2
(iii) Al2O3.x H2O → Al2O3 + x H2O
(iv) ZnS + 3/2O2 → ZnO + SO2
Solution:
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers.
22. For the metallurgical process of which of the ores calcined ore can be reduced
by carbon?
(i) haematite
(ii) calamine
(iii) iron pyrites
(iv) sphalerite
Solution:
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers.
23. The main reactions occurring in the blast furnace during the extraction of iron from
haematite are ________.
(i) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
(ii) FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
(iii) Fe2O3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO
(iv) CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
Solution:
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers
24. In which of the following method of purification, metal is converted to its volatile
compound which is decomposed to give pure metal?
(i) heating with a stream of carbon monoxide.
(ii) heating with iodine.
(iii) liquation.
(iv) distillation.
Solution:
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers.
25. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) A depressant prevents a certain type of particle to come to the froth.
(ii) Copper matte contains Cu2S and ZnS.
(iii) The solidified copper obtained from the reverberatory furnace has blistered
appearance due to evolution of SO2
during the extraction.
(iv) Zinc can be extracted by self-reduction.
Solution:
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers.
26. In the extraction of chlorine from brine _____________.
A. ΔG° for the overall reaction is negative.
B. ΔG° for the overall reaction is positive.
C. E° for the overall reaction has a negative value.
D. E° for the overall reaction has a positive value.
Solution:
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers.
III. NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 – Short Answer Type
27. Why is an external emf of more than 2.2V required for the extraction of Cl2 from brine?
Solution:
2Cl– (aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2OH– (aq) + H2(g) + Cl2(g)
The ΔGᶱ for this reaction is +422kJmol-1.
Using the formula, ΔGᶱ = -nFE°
E° = 422 x 103/2×96500
we get = -2.2V
For the reaction to take place the external voltage should be greater than 2.2V otherwise the reaction will not happen.
28. At temperatures above 1073K coke can be used to reduce FeO to Fe. How can you justify this reduction with the Ellingham diagram?
Solution:
The ∆G for the formation of FeO is less negative than ∆G for the formation of carbon monoxide from carbon. The summation of both the ∆G will be negative about 1073K. Above 1073K the line for the formation of FeO lies above the line for the oxidation of C to CO.
So, in this range, coke will be reducing the FeO and will itself be oxidised to CO.
FeO + C → Fe + CO
29. Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. Write a reaction used for the preparation of wrought iron from cast iron. How can the impurities of sulphur, silicon and phosphorus be removed from cast iron?
Solution:
Fe2O3 + 3 C → 2 Fe + 3CO
Limestone is added as a flux to remove the impurities of sulphur, silicon and phosphorous. They form a slag which can be easily removed. The metal is removed from the slag by passing through rollers.
30. How is copper extracted from low-grade copper ores?
Solution:
Copper is extracted by hydrometallurgy from low-grade copper ores. Cu is treated with scrap iron or H2. It is leached out with acid.
Cu2+(aq) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + 2H+(aq)
31. Write two basic requirements for refining of metal by Mond process and by Van Arkel Method.
Solution:
(i) The metal should react easily with the reagent to form the complex.
(ii) The volatile complex should easily decompose and not give any side products and the recovery should also be easy.
32. Although carbon and hydrogen are better-reducing agents they are not used to reduce metallic oxides at high temperatures. Why?
Carbon and hydrogen will not reduce oxides to metals but they will instead form hydrides and carbides. Therefore, they are not used as reducing agents.
33. How do we separate two sulphide ores by Froth Floatation Method? Explain with an example.
Solution:
Two sulphide ores competing to come to the froth can be separated by adjusting the oil to water proportion or by adding a depressant like NaCN. If we have two sulphide ores, ZnS and PbS, NaCN will prevent ZnS from coming to the froth and instead PbS will form the froth. This way the two ores can be separated.
34. The purest form of iron is prepared by oxidising impurities from cast iron in a reverberatory furnace. Which iron ore is used to line the furnace? Explain by giving a reaction.
Solution:
Haematite ore (Fe2O3) is the iron ore used to line the reverberatory furnace.
Fe2O3 + 3 C → 2 Fe + 3CO
Haematite is reduced by coke to wrought iron and the coke gets oxidised to CO.
35. The mixture of compounds A and B is passed through a column of Al2O3 by using alcohol as eluant. Compound A is eluted in preference to compound B. Which of the compounds A or B, is more readily adsorbed on the column?
Solution:
Compound A doesn’t adsorb on the column well and moves down the column with alcohol (eluant), while compound B gets adsorbed well on the column and cannot move down.
36. Why is sulphide ore of copper heated in a furnace after mixing with silica?
Solution:
Sulphide ore of copper is heated in a furnace after mixing with silica because the iron impurities present in the ore can form slag with silica and will be easily removed. The copper is produced as copper matte.
FeO + SiO2→ FeSiO3(slag)
37. Why are sulphide ores converted to oxide before reduction?
Solution:
Sulphide ores cannot be easily reduced so they are usually converted to oxides because oxides can be reduced easily.
38. Which method is used for refining Zr and Ti? Explain with the equation.
Solution:
Van Arkel method is used for refining Zr and Ti. Van Arkel process involves heating the impure metal with Iodine. It forms a volatile complex which on decomposition at high temperatures, gives back the metal but in very pure form.
Refining of Zr and Ti using Van Arkel method
For Zirconium,
Zr(impure) + 2I2→ ZrI4
ZrI4→Zr(pure) + 2I2 (at 1800K)
For Titanium,
Ti(impure) + 2I2→ TiI4
TiI4 → Ti(pure) + 2I2 (at 1800K)
39. What should be the considerations during the extraction of metals by electrochemical method?
Solution:
(i) Reactivity of the metal produced
(ii) Electrodes to be made of suitable material
(iii) Addition of flux for making molten mass conducting
40. What is the role of flux in metallurgical processes?
Solution:
To remove gangue, certain substances are mixed with it. These are called fluxes. Flux can be basic or acidic. Acidic flux removes basic impurity and basic flux removes acidic impurity. Flux is also used for increased conductivity.
41. How are metals used as semiconductors refined? What is the principle of the method used?
Solution:
Semiconductors are refined by zone refining. Zone refining is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten metal than in the solid metal. A molten zone moves along the impure rod heating it, the impurities dissolve in the molten zone and move along the rod, while the pure metal devoid of impurities gets left behind and crystallises out.
42. Write down the reactions taking place in Blast furnace-related to the metallurgy of iron in the temperature range 500-800 K.
Solution:
These are the reactions that happen in the blast furnace at the 500K-800K range.
3Fe2O3 + CO → 2Fe3O4 + CO2
Fe3O4 + CO →3FeO + 2CO2
Fe2O3 + CO → 2FeO + CO2
43. Give two requirements for vapour phase refining.
Solution:
(i) The metal should react easily with the reagent to form the complex.
(ii) The volatile complex should easily decomposable so that the recovery is easy.
44. Write the chemical reactions involved in the extraction of gold by the cyanide process. Also, give the role of zinc in the extraction.
Solution:
4Au(s) + 8CN– (aq) + 2H2O(aq) + O2(g) → 4[Au(CN)2] – (aq) + 4OH– (aq)
2[Au(CN)2] – (aq) + Zn(s) → 2Au(s) + [Zn(CN)4] 2– (aq)
Zinc places the role of a reducing agent. It reduces Au+ to pure Au.
IV. NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 – Matching Type
Note: Match the items given in Column I and Column II in the following
questions.
45. Match the items of Column I with items of Column II and assign the correct code:
| Column I
(A) Pendulum (B) Malachite (C) Calamine (D) Cryolite |
Column II
(1) Chrome steel (2) Nickel steel (3) Na3AlF6 (4) CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 (5) ZnCO3 |
|---|
Code :
(i) A (1) B (2) C (3) D (4)
(ii) A (2) B (4) C (5) D (3)
(iii) A (2) B (3) C (4) D (5)
(iv) A (4) B (5) C (3) D (2)
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
46. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct
code :
| Column I
(A) Coloured bands (B) Impure metal to volatile complex (C) Purification of Ge and Si (D) Purification of mercury |
Column II
(1) Zone refining (2)Fractional distillation (3) Mond Process (4) Chromatography (5) Liquation |
|---|
Code :
(i) A (1) B (2) C (4) D (5)
(ii) A (4) B (3) C (1) D (2)
(iii) A (3) B (4) C (2) D (1)
(iv) A (5) B (4) C (3) D (2)
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
47. Match items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct
code :
| Column I
(A) Cyanide process (B) Froth Floatation Process (C) Electrolytic reduction (D) Zone refining |
Column II
(1) Ultrapure Ge (2) Dressing of ZnS (3) Extraction of Al (4) Extraction of Au (5) Purification of Ni |
|---|
Code :
(i) A (4) B (2) C (3) D (1)
(ii) A (2) B (3) C (1) D (5)
(iii) A (1) B (2) C (3) D (4)
(iv) A (3) B (4) C (5) D (1)Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
48. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct
code :
| Column I
(A) Sapphire (B) Sphalerite (C) Depressant (D) Corundum |
Column II
(1) Al2O3 (2) NaCN (3) Co (4) ZnS (5) Fe2O3 |
|---|
Code :
(i) A (3) B (4) C (2) D (1)
(ii) A (5) B (4) C (3) D (2)
(iii) A (2) B (3) C (4) D (5)
(iv) A (1) B (2) C (3) D (4)
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
49. Match the items of Column I with items of Column II and assign the correct
code :
| Column I
(A) Blistered Cu (B) Blast furnace (C) Reverberatory furnace (D) Hall-Heroult process |
Column II
(1) Aluminium (2) 2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2 (3) Iron (4) FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3 (5) 2Cu2S + 3O2→ 2Cu2O + 2SO2 |
|---|
Code :
(i) A (2) B (3) C (4) D (1)
(ii) A (1) B (2) C (3) D (5)
(iii) A (5) B (4) C (3) D (2)
(iv) A (4) B (5) C (3) D (2)
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
V. NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 – Assertion and Reason Type
Note: In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a
statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following
choices.
(i) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation
of assertion.
(ii) Both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation
of assertion.
(iii) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
(iv) The assertion is false but the reason is true.
(v) Assertion and reason both are wrong.
50. Assertion: Nickel can be purified by the Mond process.
Reason: Ni (CO)4
is a volatile compound which decomposes at 460K
to give pure Ni.
Solution:
Option (i) is correct.
51. Assertion: Zirconium can be purified by Van Arkel method.
Reason: ZrI4
is volatile and decomposes at 1800K.Solution:
Option (i) is correct.
52. Assertion: Sulphide ores are concentrated by Froth Flotation method.
Reason: Cresols stabilise the froth in the Froth Flotation Method.
Solution:
Option (ii) is correct.
53. Assertion: Zone refining method is very useful for producing
semiconductors.
Reason: Semiconductors are of high purity.
Solution:
Option (ii) is correct.
54. Assertion: Hydrometallurgy involves dissolving the ore in a suitable reagent
followed by precipitation by a more electropositive metal.
Reason: Copper is extracted by hydrometallurgy.
Solution:
Option (ii) is correct.
NCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Science
The NCERT exemplars are an effective study material for scoring higher marks in the examination paper. Students must practise these additional questions for their own benefits, as these are curated by the best subject-matter experts to boost both knowledge and confidence. Students can easily access the ncert exemplar for class 12 science by visiting our website SimplyAcad and solve all the questions listed to secure maximum marks.
Here are some other NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry:
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 1 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 7 |
|---|---|
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 2 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 8 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 3 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 9 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 4 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 10 |
| NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 5 | NCERT exemplar for class 12 chemistry Chapter 11 |
latest video
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua




