NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 Linear Inequalities
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 – Linear Inequalities

NCERT solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities are prominent in imparting a clear and accurate knowledge of the subject. The topic of linear inequalities and their application are well explained with the help of NCERT exercises solutions Linear inequalities deal with the study of expressions that involve comparing any two values by an inequality symbol such as, ‘<’, ‘>’, ‘≤’ or ‘≥’. The compared values can be numerical, algebraic, or a combination of both.There are definitions, theorems, practical problems, and examples provided in this chapter that will aid in memorizing the concepts better. Thus, practicing and learning this chapter will ensure a better exam score
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 Linear Inequalities Exercise 5.1
Exercise 5.1 of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 – Linear Inequalities is based on the following topics:
- Introduction to Linear Inequalities
- Inequalities
- Algebraic Solutions of Linear Inequalities in 1 Variable and Their Graphical Representation

1. Solve 24x < 100, when
(i) x is a natural number.
(ii) x is an integer.
Solution:
(i) Given that 24x < 100
Now, we have to divide the inequality by 24, and we get x < 25/6
When x is a natural integer, then
It is clear that the only natural number less than 25/6 are 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Thus, 1, 2, 3, and 4 will be the solution of the given inequality when x is a natural number.
Hence, {1, 2, 3, 4} is the solution set.
(ii) Given that 24x < 100
Now, we have to divide the inequality by 24, and we get x < 25/6
When x is an integer, then
It is clear that the integer number less than 25/6 are…-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
Thus, the solution of 24 x < 100 is…,-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, when x is an integer.
Hence, {…, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4} is the solution set.
2. Solve – 12x > 30, when
(i) x is a natural number.
(ii) x is an integer.
Solution:
(i) Given that – 12x > 30
Now by dividing the inequality by -12 on both sides, we get x < -5/2
When x is a natural integer, then
It is clear that there is no natural number less than -2/5 because -5/2 is a negative number, and natural numbers are positive numbers.
Therefore, there would be no solution to the given inequality when x is a natural number.
(ii) Given that – 12x > 30
Now by dividing the inequality by -12 on both sides, we get x < -5/2
When x is an integer, then
It is clear that the integer number less than -5/2 are…, -5, -4, – 3
Thus, the solution of – 12x > 30 is …,-5, -4, -3, when x is an integer.
Therefore, the solution set is {…, -5, -4, -3}.
3. Solve 5x – 3 < 7, when
(i) x is an integer
(ii) x is a real number
Solution:
(i) Given that, 5x – 3 < 7
Now by adding 3 on both sides, we get
5x – 3 + 3 < 7 + 3
Above inequality becomes
5x < 10
Again, by dividing both sides by 5, we get
5x/5 < 10/5
x < 2
When x is an integer, then
It is clear that the integer numbers less than 2 are…, -2, -1, 0, 1.
Thus, the solution of 5x – 3 < 7 is …,-2, -1, 0, 1, when x is an integer.
Therefore, the solution set is {…, -2, -1, 0, 1}
(ii) Given that, 5x – 3 < 7
Now by adding 3 on both sides, we get
5x – 3 + 3 < 7 + 3
Above inequality becomes
5x < 10
Again, by dividing both sides by 5, we get,
5x/5 < 10/5
x < 2
When x is a real number, then
It is clear that the solutions of 5x – 3 < 7 will be given by x < 2, which states that all the real numbers are less than 2.
Hence, the solution set is x ∈ (-∞, 2).
4. Solve 3x + 8 >2, when
(i) x is an integer.
(ii) x is a real number.
Solution:
(i) Given that 3x + 8 > 2
Now, by subtracting 8 from both sides, we get
3x + 8 – 8 > 2 – 8
The above inequality becomes,
3x > – 6
Again, by dividing both sides by 3, we get
3x/3 > -6/3
Hence x > -2
When x is an integer, then
It is clear that the integer number greater than -2 are -1, 0, 1, 2,…
Thus, the solution of 3x + 8 > 2 is -1, 0, 1, 2,… when x is an integer.
Hence, the solution set is {-1, 0, 1, 2,…}
(ii) Given that, 3x + 8 > 2
Now, by subtracting 8 from both sides, we get
3x + 8 – 8 > 2 – 8
The above inequality becomes,
3x > – 6
Again, by dividing both sides by 3, we get
3x/3 > -6/3
Hence x > -2
When x is a real number.
It is clear that the solutions of 3x + 8 >2 will be given by x > -2, which states that all the real numbers are greater than -2.
Therefore, the solution set is x ∈ (-2, ∞).
Solve the inequalities in Exercises 5 to 16 for real x.
5. 4x + 3 < 5x + 7
Solution:
Given that, 4x + 3 < 5x + 7
Now by subtracting 7 from both sides, we get
4x + 3 – 7 < 5x + 7 – 7
The above inequality becomes,
4x – 4 < 5x
Again, by subtracting 4x from both sides,
4x – 4 – 4x < 5x – 4x
x > – 4
∴ The solutions of the given inequality are defined by all the real numbers greater than -4.
Hence, the required solution set is (-4, ∞).
6. 3x – 7 > 5x – 1
Solution:
Given that,
3x – 7 > 5x – 1
Now by adding 7 to both sides, we get
3x – 7 +7 > 5x – 1 + 7
3x > 5x + 6
Again, by subtracting 5x from both sides,
3x – 5x > 5x + 6 – 5x
-2x > 6
Dividing both sides by -2 to simplify, we get
-2x/-2 < 6/-2
x < -3
∴ The solutions of the given inequality are defined by all the real numbers less than -3.
Hence, the required solution set is (-∞, -3).
7. 3(x – 1) ≤ 2 (x – 3)
Solution:
Given that, 3(x – 1) ≤ 2 (x – 3)
By multiplying the above, inequality can be written as
3x – 3 ≤ 2x – 6
Now, by adding 3 to both sides, we get
3x – 3+ 3 ≤ 2x – 6+ 3
3x ≤ 2x – 3
Again, by subtracting 2x from both sides,
3x – 2x ≤ 2x – 3 – 2x
x ≤ -3
Therefore, the solutions of the given inequality are defined by all the real numbers less than or equal to -3.
Hence, the required solution set is (-∞, -3].
8. 3 (2 – x) ≥ 2 (1 – x)
Solution:
Given that, 3 (2 – x) ≥ 2 (1 – x)
By multiplying, we get
6 – 3x ≥ 2 – 2x
Now, by adding 2x to both sides,
6 – 3x + 2x ≥ 2 – 2x + 2x
6 – x ≥ 2
Again, by subtracting 6 from both sides, we get
6 – x – 6 ≥ 2 – 6
– x ≥ – 4
Multiplying inequality by a negative sign, we get
x ≤ 4
∴ The solutions of the given inequality are defined by all the real numbers greater than or equal to 4.
Hence, the required solution set is (-∞, 4].
9. x + x/2 + x/3 < 11
Solution:


x < 6
The solutions of the given inequality are defined by all the real numbers less than 6.
Hence, the solution set is (-∞, 6).
10. x/3 > x/2 + 1
Solution:

– x/6 > 1
– x > 6
x < – 6
∴ The solutions of the given inequality are defined by all the real numbers less than – 6.
Hence, the required solution set is (-∞, -6).
11. 3(x – 2)/5 ≤ 5 (2 – x)/3
Solution:
Given that,
![]()
Now by cross-multiplying the denominators, we get
9(x- 2) ≤ 25 (2 – x)
9x – 18 ≤ 50 – 25x
Now adding 25x on both sides,
9x – 18 + 25x ≤ 50 – 25x + 25x
34x – 18 ≤ 50
Adding 25x on both sides,
34x – 18 + 18 ≤ 50 + 18
34x ≤ 68
Dividing both sides by 34,
34x/34 ≤ 68/34
x ≤ 2
The solutions of the given inequality are defined by all the real numbers less than or equal to 2.
Hence, the required solution set is (-∞, 2].
![]()
Solution:

120 ≥ x
∴ The solutions of the given inequality are defined by all the real numbers less than or equal to 120.
Thus, (-∞, 120] is the required solution set.
13. 2 (2x + 3) – 10 < 6 (x – 2)
Solution:
Given that,
2 (2x + 3) – 10 < 6 (x – 2)
By multiplying, we get
4x + 6 – 10 < 6x – 12
On simplifying, we get
4x – 4 < 6x – 12
4x – 6x < -12 + 4
-2x < -8
Dividing by 2, we get;
-x < -4
Multiply by “-1” and change the sign.
x > 4
∴ The solutions of the given inequality are defined by all the real numbers greater than 4.
Hence, the required solution set is (4, ∞).
14. 37 – (3x + 5) ≥ 9x – 8 (x – 3)
Solution:
Given that, 37 – (3x + 5) ≥ 9x – 8 (x – 3)
On simplifying, we get
= 37 – 3x – 5 ≥ 9x – 8x + 24
= 32 – 3x ≥ x + 24
On rearranging
= 32 – 24 ≥ x + 3x
= 8 ≥ 4x
= 2 ≥ x
All the real numbers of x which are less than or equal to 2 are the solutions to the given inequality
Hence, (-∞, 2] will be the solution for the given inequality.
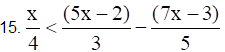
Solution:
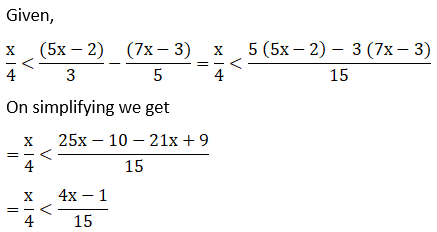
= 15x < 4 (4x – 1)
= 15x < 16x – 4
= 4 < x
All the real numbers of x which are greater than 4 are the solutions of the given inequality.
Hence, (4, ∞) will be the solution for the given inequality.

Solution:

![]()
= 20 (2x – 1) ≥ 3 (19x – 18)
= 40x – 20 ≥ 57x – 54
= – 20 + 54 ≥ 57x – 40x
= 34 ≥ 17x
= 2 ≥ x
∴ All the real numbers of x, which are less than or equal to 2, are the solutions to the given inequality.
Hence, (-∞, 2] will be the solution for the given inequality.
Solve the inequalities in Exercises 17 to 20 and show the graph of the solution in each case on a number line.
17. 3x – 2 < 2x + 1
Solution:
Given,
3x – 2 < 2x + 1
Solving the given inequality, we get
3x – 2 < 2x + 1
= 3x – 2x < 1 + 2
= x < 3
Now, the graphical representation of the solution is as follows:

18. 5x – 3 ≥ 3x – 5
Solution:
We have,
5x – 3 ≥ 3x – 5
Solving the given inequality, we get
5x – 3 ≥ 3x – 5
On rearranging, we get
= 5x – 3x ≥ -5 + 3
On simplifying
= 2x ≥ -2
Now, by dividing 2 on both sides, we get
= x ≥ -1
The graphical representation of the solution is as follows:

19. 3 (1 – x) < 2 (x + 4)
Solution:
Given,
3 (1 – x) < 2 (x + 4)
Solving the given inequality, we get
3 (1 – x) < 2 (x + 4)
On multiplying, we get
= 3 – 3x < 2x + 8
On rearranging, we get
= 3 – 8 < 2x + 3x
= – 5 < 5x
Now, by dividing 5 on both sides, we get
-5/5 < 5x/5
= – 1 < x
Now, the graphical representation of the solution is as follows:


Solution:
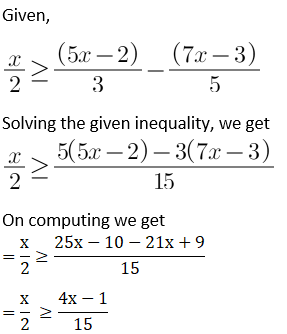

On computing, we get
![]()
= 15x ≥ 2 (4x – 1)
= 15x ≥ 8x -2
= 15x -8x ≥ 8x -2 -8x
= 7x ≥ -2
= x ≥ -2/7
Now, the graphical representation of the solution is as follows:

21. Ravi obtained 70 and 75 marks in the first two unit tests. Find the minimum marks he should get in the third test to have an average of at least 60 marks.
Solution:
Let us assume x be the marks obtained by Ravi in his third unit test
According to the question, the entire students should have an average of at least 60 marks
(70 + 75 + x)/3 ≥ 60
= 145 + x ≥ 180
= x ≥ 180 – 145
= x ≥ 35
Hence, all the students must obtain 35 marks in order to have an average of at least 60 marks.
22. To receive a Grade ‘A’ in a course, one must obtain an average of 90 marks or more in five examinations (each of 100 marks). If Sunita’s marks in the first four examinations are 87, 92, 94 and 95, find the minimum marks that Sunita must obtain in the fifth examination to get a Grade ‘A’ in the course.
Solution:
Let us assume Sunita scored x marks in her fifth examination
Now, according to the question, in order to receive a Grade ‘A’ in the course, she must have to obtain an average of 90 marks or more in her five examinations
(87 + 92 + 94 + 95 + x)/5 ≥ 90
= (368 + x)/5 ≥ 90
= 368 + x ≥ 450
= x ≥ 450 – 368
= x ≥ 82
Hence, she must have to obtain 82 or more marks in her fifth examination to get a Grade ‘A’ in the course.
23. Find all pairs of consecutive odd positive integers, both of which are smaller than 10, such that their sum is more than 11.
Solution:
Let us assume x be the smaller of the two consecutive odd positive integers
∴ Other integer is = x + 2
It is also given in the question that both the integers are smaller than 10
∴ x + 2 < 10
x < 8 … (i)
Also, it is given in the question that the sum of two integers is more than 11
∴ x + (x + 2) > 11
2x + 2 > 11
x > 9/2
x > 4.5 … (ii)
Thus, from (i) and (ii), we have x as an odd integer, which can take values 5 and 7.
Hence, possible pairs are (5, 7) and (7, 9)
24. Find all pairs of consecutive even positive integers, both of which are larger than 5, such that their sum is less than 23.Solution:
Let us assume x be the smaller of the two consecutive even positive integers
∴ Other integer = x + 2
It is also given in the question that both the integers are larger than 5
∴ x > 5 ….(i)
Also, it is given in the question that the sum of two integers is less than 23.
∴ x + (x + 2) < 23
2x + 2 < 23
x < 21/2
x < 10.5 …. (ii)
Thus, from (i) and (ii), we have x as an even number, which can take values 6, 8 and 10.
Hence, possible pairs are (6, 8), (8, 10) and (10, 12).
25. The longest side of a triangle is 3 times the shortest side, and the third side is 2 cm shorter than the longest side. If the perimeter of the triangle is at least 61 cm, find the minimum length of the shortest side.
Solution:
Let us assume the length of the shortest side of the triangle to be x cm
∴ According to the question, the length of the longest side = 3x cm
And, length of third side = (3x – 2) cm
As the least perimeter of the triangle = 61 cm
Thus, x + 3x + (3x – 2) cm ≥ 61 cm
= 7x – 2 ≥ 61
= 7x ≥ 63
Now divide by 7, and we get
= 7x/7 ≥ 63/7
= x ≥ 9
Hence, the minimum length of the shortest side will be 9 cm.
26. A man wants to cut three lengths from a single piece of board of length 91cm.
The second length is to be 3cm longer than the shortest, and the third length is to be twice as long as the shortest. What are the possible lengths of the shortest board if the third piece is to be at least 5cm longer than the second?
Solution:
Let us assume the length of the shortest piece to be x cm
∴ According to the question, the length of the second piece = (x + 3) cm
And, the length of the third piece = 2x cm
As all three lengths are to be cut from a single piece of the board having a length of 91 cm
∴ x + (x + 3) + 2x ≤ 91 cm
= 4x + 3 ≤ 91
= 4x ≤ 88
= 4x/4 ≤ 88/4
= x ≤ 22 … (i)
Also, it is given in the question that the third piece is at least 5 cm longer than the second piece
∴ 2x ≥ (x+3) + 5
2x ≥ x + 8
x ≥ 8 … (ii)
Thus, from equations (i) and (ii), we have:
8 ≤ x ≤ 22
Hence, it is clear that the length of the shortest board is greater than or equal to 8 cm and less than or equal to 22 cm.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 Linear Inequalities– Exercise 5.2
Exercise 5.2 of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 – Linear Inequalities
This exercise contains questions related to Graphical Solution of Linear Inequalities in Two Variables.

Solve the following inequalities graphically in a two-dimensional plane.
1. x + y < 5
Solution:
Given, x + y < 5
Consider,
| X | 0 | 5 |
| y | 5 | 0 |
Now, draw a dotted line x + y = 5 in the graph (∵ x + y = 5 is excluded in the given question.)
Now, consider x + y < 5
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ 0 + 0 < 5
⇒ 0 < 5 (this is true)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is below the line x + y = 5. (That is, the origin is included in the region.)
The graph is as follows:
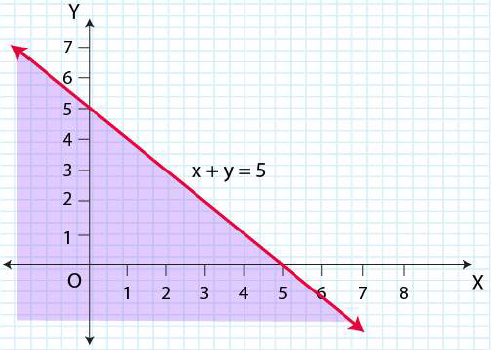
2. 2x + y ≥ 6
Solution:
Given 2x + y ≥ 6
Now, draw a solid line 2x + y = 6 in the graph (∵ 2x + y = 6 is included in the given question.)
Now, consider 2x + y ≥6
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ 2 × (0) + 0 ≥ 6
⇒ 0 ≥ 6 (This is false.)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is above the line 2x + y = 6. (Away from the origin.)
The graph is as follows:

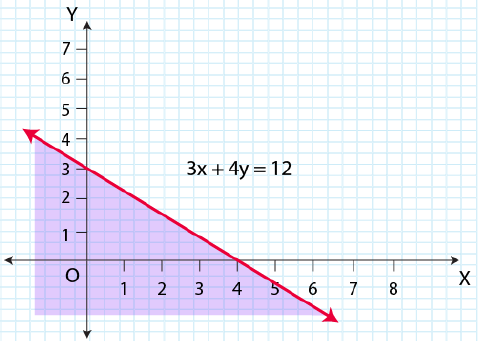
3. 3x + 4y ≤ 12
Solution:
Given, 3x + 4y ≤ 12
Now, draw a solid line 3x + 4y = 12 in the graph (∵ 3x + 4y = 12 is included in the given question.)
Now, consider 3x + 4y ≤ 12
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ 3 × (0) + 4 × (0) ≤ 12
⇒ 0 ≤ 12 (This is true.)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is below the line 3x + 4y = 12. (That is, the origin is included in the region.)
The graph is as follows:
4. y + 8 ≥ 2x
Solution:
Given, y + 8 ≥ 2x
Now, draw a solid line y + 8 = 2x in the graph (∵ y + 8 = 2x is included in the given question.)
Now, consider y + 8 ≥ 2x
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ (0) + 8 ≥ 2 × (0)
⇒ 0≤ 8 (This is true.)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is above the line y + 8 = 2x. (That is, the origin is included in the region.)
The graph is as follows:

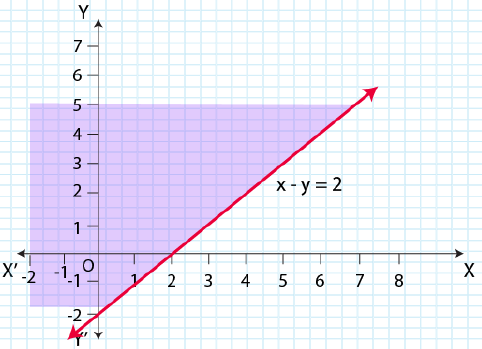
5. x – y ≤ 2
Solution:
Given, x – y ≤ 2
Now, draw a solid line x – y = 2 in the graph (∵ x – y = 2 is included in the given question.)
Now, consider x – y ≤ 2
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ (0) – (0) ≤ 2
⇒ 0 ≤ 2 (This is true.)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is above the line x – y = 2. (That is, the origin is included in the region.)
The graph is as follows:
6. 2x – 3y > 6
Solution:
Given, 2x – 3y > 6
Now, draw a dotted line 2x – 3y = 6 in the graph (∵ 2x – 3y = 6 is excluded in the given question.)
Now, consider 2x – 3y > 6
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ 2 × (0) – 3 × (0) > 6
⇒ 0 > 6 (This is false.)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is below the line 2x – 3y > 6. (Away from the origin.)
The graph is as follows:

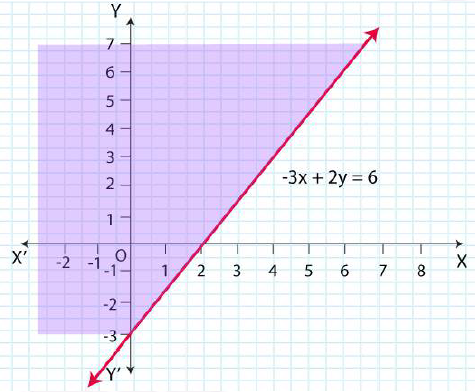
7. – 3x + 2y ≥ – 6
Solution:
Given, – 3x + 2y ≥ – 6
Now, draw a solid line – 3x + 2y = – 6 in the graph (∵– 3x + 2y = – 6 is included in the given question.)
Now, consider – 3x + 2y ≥ – 6
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ – 3 × (0) + 2 × (0) ≥ – 6
⇒ 0 ≥ – 6 (This is true.)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is above the line – 3x + 2y ≥ – 6. (That is, the origin
is included in the region)
The graph is as follows:
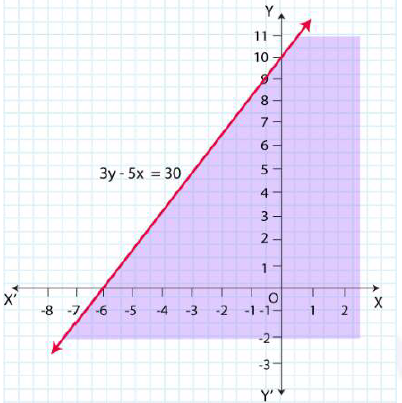
8. y – 5x < 30
Solution:
Given, y – 5x < 30
Now, draw a dotted line 3y – 5x = 30 in the graph (∵3y – 5x = 30 is excluded in the given question.)
Now, consider 3y – 5x < 30
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ 3 × (0) – 5 × (0) < 30
⇒ 0 < 30 (This is true.)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is below the line 3y – 5x < 30. (That is, the origin is included in the region.)
The graph is as follows:
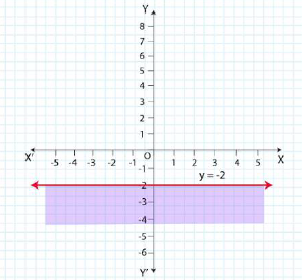
9. y < – 2
Solution:
Given, y < – 2
Now, draw a dotted line y = – 2 in the graph (∵ y = – 2 is excluded in the given question.)
Now, consider y < – 2
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ 0 < – 2 (This is false)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is below the line y < – 2. (That is, away from the origin.)
The graph is as follows:
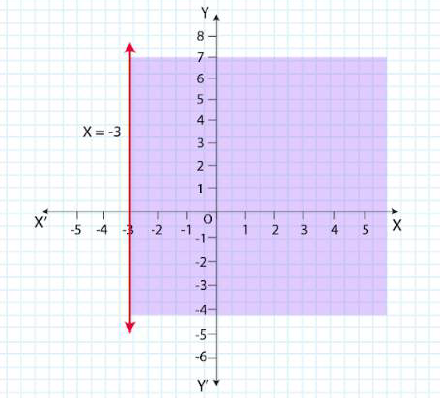
10. x > – 3
Solution:
Given, x > – 3
Now, draw a dotted line x = – 3 in the graph (∵x = – 3 is excluded in the given question.)
Now, consider x > – 3
Select a point (0, 0).
⇒ 0 > – 3
⇒ 0 > – 3 (This is true.)
∴ The solution region of the given inequality is right to the line x > – 3. (That is, the origin is included in the region.)
The graph is as follows:
latest video
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua





